Expressvpn Glossary
Two-factor authentication (2FA)
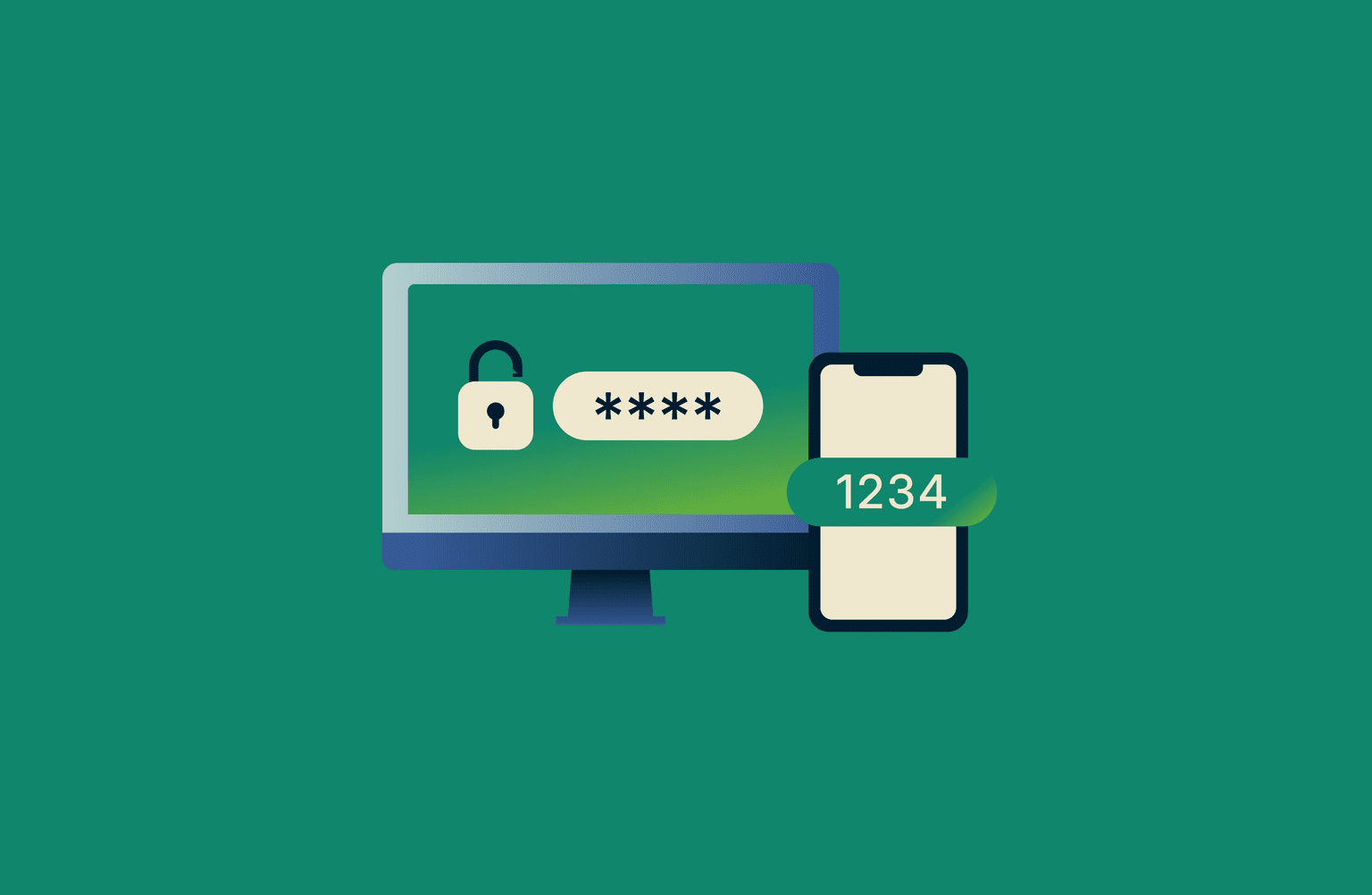

What is two-factor authentication?
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is a security process that uses two types of identification to verify a user’s identity. The first factor is something the user knows, such as a password, and the second is something the user has or is, such as a verification code or biometric feature.
Its core purpose is to add an extra layer of account protection beyond a password, reducing the likelihood of unauthorized access if login credentials are compromised.
How does two-factor authentication work?
2FA verifies identity in two steps:
- Enter username and password: The user signs in with a username and password, which serve as the first factor (something known). If these credentials are valid, the system proceeds to the next step.
- Confirm identity with a second factor: A second factor confirms identity through a code, app, email, or biometric check, adding another layer of protection before access is granted.
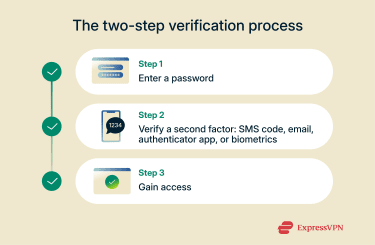
2FA can use different methods for the second verification step:
- SMS codes: A one-time code sent by text message; easy to implement but less secure if the phone number is compromised.
- Email verification: A code or link sent to the user’s email address; overall security depends on the protection of the email account.
- Authenticator apps: Applications such as Google Authenticator or Authy generate verification codes locally on the device; they are more secure than SMS and work without network access.
- Biometrics: Fingerprint, facial recognition, or voice verification based on physical traits; convenient but dependent on compatible and trusted devices.
Why is two-factor authentication important?
By adding a second verification step, 2FA protects accounts even if passwords are stolen. It helps prevent unauthorized access from phishing or brute-force attacks and provides stronger security for sensitive data and online services.
Common use cases
2FA is used across online services that handle sensitive or personal data. Common examples include:
- Email accounts and cloud storage: Protects messages, files, and other stored information.
- Online banking and financial apps: Verifies account ownership during logins or transactions.
- Social media platforms: Prevents unauthorized access, profile takeovers, and identity misuse.
- Workplace logins and corporate virtual private network (VPN) access: Secures employee access to internal systems and company networks.
Benefits and limitations
The main benefits of 2FA include:
- Adding an extra verification step beyond a password.
- Protecting accounts even if passwords are leaked or stolen.
- Providing stronger security for sensitive data and online services.
However, there are also some limitations:
- Certain methods rely on mobile networks or specific devices.
- SMS verification can be vulnerable to SIM swapping or phone loss.
- Losing a device may temporarily block access.
Further reading
- What is two-factor authentication (2FA), and how to set it up securely
- 2FA vs. MFA: Key differences and how to choose the right one
- Why should I use two-factor authentication?
- How to add and generate two-factor authentication (2FA) codes in ExpressVPN Keys
FAQ
What is the difference between 2FA and MFA?
Two-factor authentication (2FA) requires exactly two verification factors, while multi-factor authentication (MFA) involves two or more. All 2FA systems are forms of MFA, but MFA can include additional verification steps beyond the second factor for stronger security.
Is two-factor authentication safe?
Yes. Two-factor authentication (2FA) significantly strengthens account protection by requiring an extra verification step. Its effectiveness depends on the method used, with authenticator apps and biometrics offering higher security than SMS codes.
What are the most common 2FA methods?
The most common methods include SMS codes, authenticator apps, email verification, and biometrics such as fingerprint or facial recognition.
Can 2FA be hacked?
Two-factor authentication (2FA) is more secure than using passwords alone, but it is not foolproof. Attackers can sometimes bypass 2FA by exploiting weak account recovery systems or compromising linked accounts, such as email. SMS-based 2FA is also vulnerable to SIM swapping, where a phone number is transferred to a device controlled by the attacker.
Using authenticator apps, biometrics, or physical security keys offers stronger protection against these methods.
