Expressvpn Glossary
IT security
What is IT security?
IT security refers to the methods, tools, and practices used to protect digital systems, networks, and data from unauthorized access, attacks, misuse, or damage. It aims to preserve the confidentiality, integrity, availability, and authenticity of data across systems and users, covering areas such as network security, cloud security, and application security.
How does IT security work?
IT security works by layering protections across hardware, software, and user practices to detect, block, and respond to threats. Common IT security solutions include firewalls that monitor network traffic, antivirus software that scans for malicious code, endpoint protection that secures individual devices, and virtual private networks (VPNs) that encrypt connections to protect data in transit.
It also involves user authentication to verify identities, Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) encryption to secure sensitive communications, and continuous monitoring to detect suspicious activity. When incidents occur, IT security teams follow a response plan to contain the threat and minimize damage. These protections apply to devices, networks, cloud environments, and applications alike.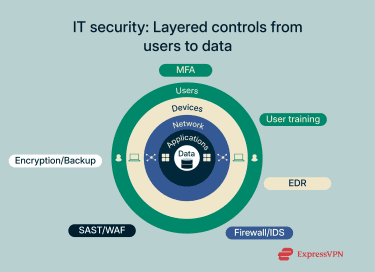
Why is IT security important?
IT security is important because it prevents data theft and unauthorized access that could lead to identity fraud or financial loss. It also safeguards transactions in online banking and e-commerce.
For businesses, it protects valuable intellectual property and minimizes the risk of malware and ransomware attacks that can halt operations. While maintaining strong IT security can be expensive, the damage from a serious breach is often far greater and can threaten a company’s survival.
Effective IT security also helps organizations stay compliant with data protection regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). Strong practices not only keep operations running but also strengthen customer trust in the business.
Where is IT security used?
IT security is applied almost everywhere technology is present, from large corporations to individual home users.
- Business environments: Companies across sectors such as retail, manufacturing, and transportation use IT security to protect internal networks, employee devices, and intellectual property.
- Cloud and SaaS services: Cloud providers and organizations using Software-as-a Service (SaaS) platforms rely on IT security to protect stored data, manage access controls, and ensure service reliability.
- Government and critical sectors: Governments and industries like finance, healthcare, and energy depend on IT security to protect sensitive public data, patient records, and critical infrastructure such as power grids.
- Personal use: Individuals rely on IT security for home Wi-Fi networks, mobile devices, laptops, and Internet of Things (IoT) devices such as smart speakers, cameras, and thermostats to prevent unauthorized access and protect private data.
Further reading
- What is cybersecurity? A simple guide for beginners
- What is a firewall, and how does it work
- VPN vs. antivirus: Key differences
FAQ
What is the difference between IT security and cybersecurity?
The key difference between IT security and cybersecurity is their scope. IT security protects all forms of information and technology assets, whether across hardware, software, or networks. Cybersecurity, on the other hand, focuses specifically on defending digital systems and data from online threats such as hacking, phishing, and malware.
What is security clearance?
Security clearance is a status granted to an individual, such as a government or cybersecurity employee, after a thorough background investigation. It confirms that a person is trusted to access, handle, and protect classified or sensitive information.
While security clearance focuses on assessing the individual, IT security focuses on the technology and systems that protect the data itself.
What are the most common IT security threats?
Common IT security threats include malware, like spyware and ransomware, that can steal, damage, or block access to data. Phishing scams that use fraudulent emails to trick users into revealing sensitive information are another threat. Distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks make an online service unavailable by overwhelming it with traffic.
Many of these threats exploit software vulnerabilities, which serve as an entry point for attackers. Protecting against them is a primary reason why IT security is important.
What tools are used in IT security?
A wide range of tools are used across various environments. These include firewalls to prevent unauthorized network access and antivirus software to detect and remove malicious software. Other tools are security information and event management (SIEM) systems for analyzing data, data loss prevention (DLP) tools to protect sensitive information, and encryption software, such as VPNs, to protect data in transit.
