Expressvpn Glossary
Database management system (DBMS)
What is a database management system?
A database management system (DBMS) is a software system that facilitates the management, storage, retrieval, and querying of data in one or more databases. Without a DBMS, data management tasks might require relying on disparate file systems or custom solutions. A DBMS simplifies these tasks, allowing users to create, update, and query databases efficiently, while ensuring data integrity, consistency, and security.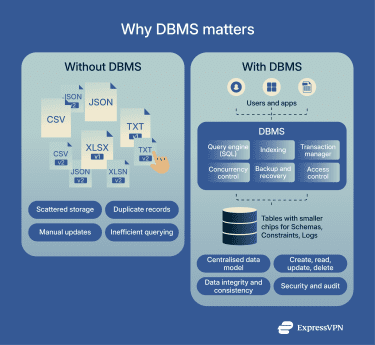
How does a database management system work?
A DBMS serves as an intermediary between one or more databases and various clients, such as applications and users. Its main purpose is to facilitate secure and efficient data interactions. Often, DBMSs rely on APIs to handle data requests, enabling apps and users to interact with the database securely and efficiently without directly accessing the data.
When a user or application makes a request, the DBMS processes it using a database access language like Structured Query Language (SQL). In the context of DBMSs, these languages consist of two primary command types:
- Data definition language (DDL): Used to define and build the database structure. The CREATE command, for example, sets up new tables, fields, and relationships.
- Data manipulation language (DML): Used to interact with the data inside the tables. Common statements include INSERT to add data, UPDATE to modify it, or DELETE to remove it.
Why is a database management system important?
DBMSs help businesses manage data more efficiently. They can enforce rules to protect data integrity and manage redundancy. For example, a DBMS might notify a user that a required field, like a name or address, can’t be empty. Another rule might prevent the duplication of data.
In many cases, DBMSs play a critical role in coordination, organizing resources to perform many business tasks, such as allowing e-commerce customers to search for merchandise and make purchases. Many also provide administrators with maintenance features, including backup, recovery, and indexing.
All of this helps businesses scale their operations. Incorporating a DBMS is central to financial, healthcare, and enterprise operations.
Where are database management systems used?
DBMSs are used in many digital environments, including:
- Web applications: E-commerce sites use DBMSs to manage products, inventory, and customer purchases. On social media sites, they’re deployed to store user profiles and posts. Reservation systems for airlines usually rely on a DBMS to manage ticket and flight information.
- Enterprise software: HR systems manage employee records, payroll, and taxes using a DBMS. At manufacturing firms, they can track parts, inventory, and the overall supply chain.
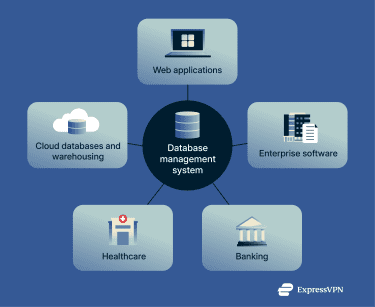
- Banking: Banks use DBMSs to record and manage customers’ records. They manage large amounts of information, including transactions, deposits, and withdrawals.
- Healthcare: Organizations in the healthcare field handle large amounts of data, from clinical information and appointment scheduling to financial records. DBMSs often play a key role in securely managing this sensitive data.
- Cloud storage: DBMSs form the basis of many cloud database and data warehousing services. They facilitate analytics, manage storage, and more.
Further reading
- What is data encryption?
- What is data anonymization? Benefits, methods, and best practices
- What is data privacy and why it matters: A complete guide
- How to remove yourself from data broker sites
FAQ
What are examples of DBMS software?
Common examples include MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Microsoft SQL Server. Though distinct technically, all of these tools are used by organizations to better manage large troves of data.
How is a DBMS different from a database?
A database is an organized collection of data. A database management system (DBMS) is a software application that provides the tools to interact with, manage, and secure that data.
What is the role of SQL in a DBMS?
Structured Query Language (SQL) is the standard language used to communicate with many database management systems (DBMSs). SQL queries are used to ask a DBMS to retrieve, update, insert, or delete data.
Is DBMS used in cloud applications?
Yes. Cloud providers offer Database-as-a-Service (DBaaS), which is a fully managed database management system (DBMS) platform. These services handle maintenance, backups, and scaling, so developers can focus on using the database.
