Expressvpn Glossary
Data breach

What is a data breach?
A data breach is a security incident where sensitive, confidential, or protected data is accessed or disclosed without authorization. Data breaches often compromise information like Social Security numbers, healthcare data, or bank account details. Attackers usually aim to steal data for financial gain.
How do data breaches happen?
Data breaches can occur for many reasons, including phishing attacks, security vulnerabilities, weak passwords, and insider threats or human error.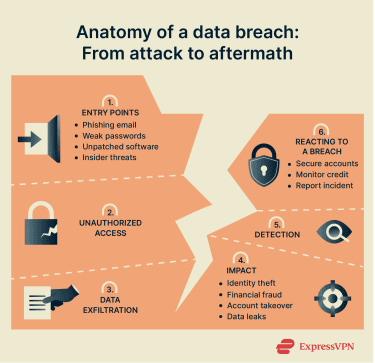
Phishing attacks
In phishing attacks, criminals trick people into revealing sensitive information, such as login credentials or financial details. These scams often arrive through fraudulent emails, texts, or instant messages that mimic legitimate sources. Clicking a link directs victims to a fake website controlled by attackers, where they may be tricked into entering their details. Once stolen, this information can be used to launch a breach.
Unpatched vulnerabilities
Software and hardware sometimes contain flaws caused by unintended interactions, coding errors, or outdated components, which can be exploited by cybercriminals. Manufacturers and developers regularly release security patches or updates to fix them, but when users and organizations fail to update promptly, attackers can exploit the gaps.
Insider threats
An insider threat comes from someone with legitimate access, such as an employee, contractor, or partner, who misuses that access. This may be intentional, such as stealing data, or accidental, through carelessness.
Poor password practices
Weak or reused passwords make it easier for attackers to break into accounts. Brute-force tools can quickly guess short, simple passwords, and if the same password is reused across accounts, one breach can unlock multiple services.
Consequences of a data breach
Data breaches can have serious consequences for both individuals and organizations:
- Identity theft: Stolen personal data can be used to open fraudulent accounts, file false tax returns, or access existing financial services.
- Financial loss: Victims may face fraudulent charges, drained bank accounts, or extortion attempts.
- Reputational damage: Businesses risk losing customer trust.
- Legal penalties: Regulators can impose fines on organizations that fail to safeguard data.
Good security hygiene, like using strong, unique passwords, enabling multi-factor authentication (MFA), and keeping software updated, reduces the risk. Encryption and virtual private networks (VPNs) add further protection by securing data while it’s in transit.
Where do data breaches occur?
Any entity that stores digital data can suffer a breach:
Major companies
High-profile data breaches usually involve large corporations with millions of user accounts. The 2017 Equifax breach, which exposed the personal information of 147 million people, and the 2013 Yahoo megabreach that affected 3 billion users, are two well-known examples.
Government agencies
Government agencies’ databases hold vast amounts of sensitive information, making them significant targets for data breaches. Among the most noteworthy government breaches is the 2015 breach at the U.S. Office of Personnel Management, which exposed the records of millions of federal employees and is considered one of the largest breaches of government data.
Cloud storage misconfigurations
Many companies use cloud services to store their data, and misconfigured cloud settings can leave vulnerabilities that lead to data breaches.
Personal accounts
While most data breaches are targeted at large-scale organizations, personal accounts, like email addresses, social media logins, and online banking accounts, can also be breached through phishing attacks or weak passwords.
Further reading
- Check if your email has been exposed in data breaches
- Why your old email is a goldmine for hackers
- Data leak on an iPhone: How to view and fix leaked passwords
- How to prevent phishing attacks: Best practices and prevention tips
- 10 phishing red flags in emails and what to do about them
- Internet hacks: Phishing and spearphishing explained
FAQ
What are common causes of data breaches?
The most common causes of data breaches are phishing attacks, weak passwords, unpatched software vulnerabilities, and insider threats.
How can I tell if my data was breached?
Signs of suspicious activity in accounts, such as unauthorized login alerts or unexpected password reset requests, can indicate a data breach. Companies that experience a breach may also notify affected individuals that their information has been compromised.
Can a VPN prevent a data breach?
A VPN can’t prevent a breach at its source, but it does improve security. By encrypting data in transit, a VPN helps protect personal information from interception and lowers the risk of exposure.
What should I do after a data breach?
Following a data breach, change affected passwords, enable two-factor authentication (2FA), report the incident, and watch financial statements for unusual activity.
