What is MU-MIMO, and why does it matter for VPN performance?

Wi-Fi has come a long way from the days when only one device could get a clear signal at a time. Today, with dozens of connected devices in most homes, from phones and laptops to smart TVs and cameras, your router works harder than ever. That’s where Multi-User, Multiple-Input, Multiple-Output (MU-MIMO) comes in.
MU-MIMO lets your router communicate with several devices simultaneously. That means smoother connections, faster speeds, and fewer slowdowns when everyone’s online.
In this guide, we’ll break down what MU-MIMO is, how it works, its benefits and limitations, and what it means for your virtual private network (VPN) speed and stability.
Understanding MU-MIMO technology
When your Wi-Fi slows down as more devices connect, the main reason is often that older routers were built to communicate with only one device at a time, like a single cashier serving a long line of customers one by one.
Before multi-user systems came along, Multiple-Input, Multiple-Output (MIMO) technology was developed to improve the quality of that one-at-a-time service. It used multiple antennas to send and receive data along different paths, helping your device get a stronger, more stable signal even when the Wi-Fi had to travel around walls or obstacles.
The limitation was that early routers used Single-User MIMO (SU-MIMO), which meant only one device could receive data at a time. Even if the cashier was fast, everyone else in line still had to wait for their turn.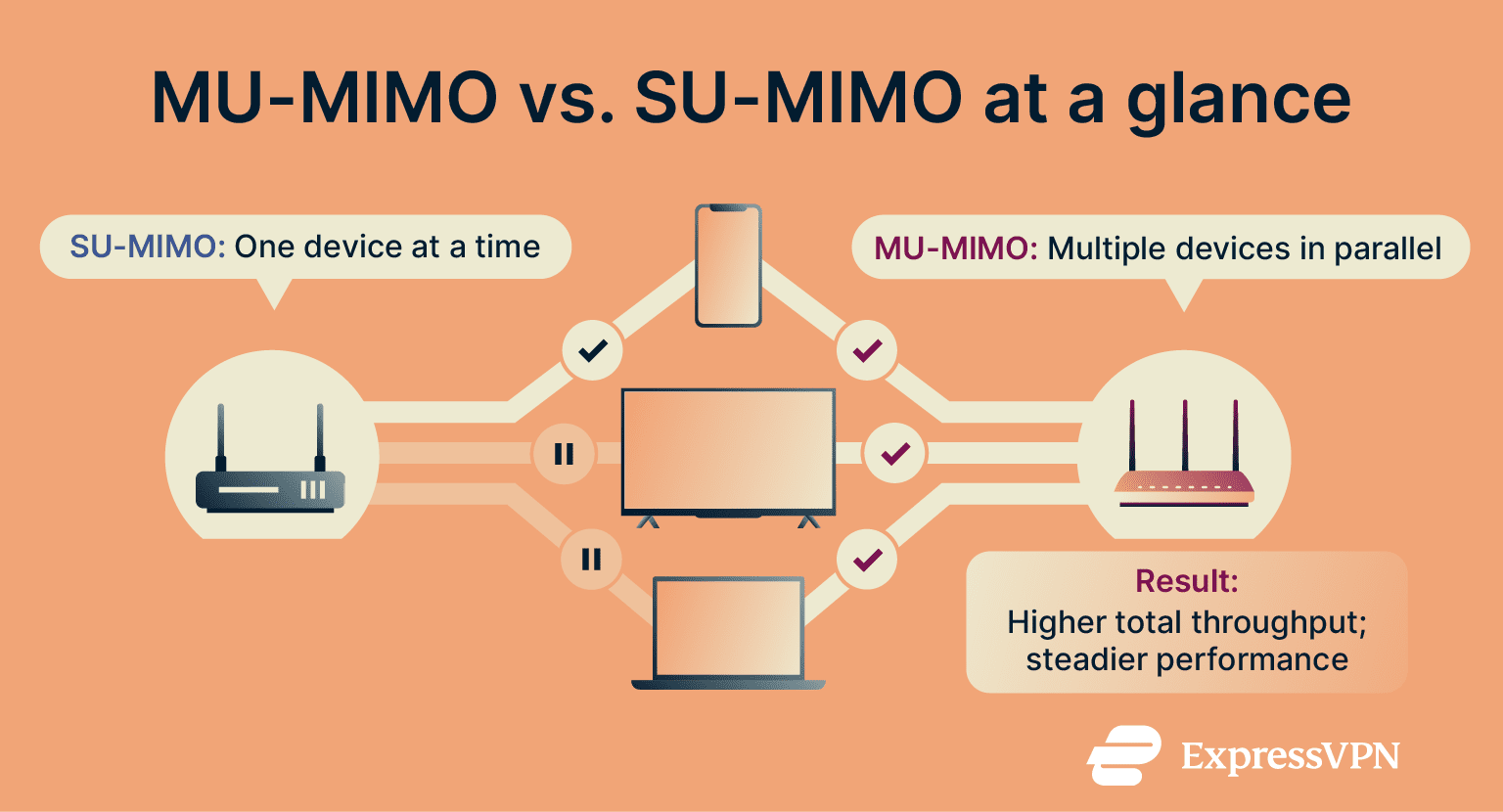
Building on that foundation, MU-MIMO was introduced. Instead of serving one device and then moving to the next, it allows a router to transmit separate data streams to several devices simultaneously. It’s the Wi-Fi equivalent of opening multiple cashier lanes.
The shift from “take turns” to “all at once” forms the foundation of modern, high-performance Wi-Fi, and it’s why newer routers feel so much faster than older ones in busy households or offices.
Simple definition of MU-MIMO
MU-MIMO acts as smart traffic control for your Wi-Fi. The technology’s name, Multi-User Multiple-Input, Multiple-Output, simply describes its primary function: enabling your router to communicate with several devices simultaneously.
The core job of MU-MIMO technology is to enable simultaneous communication, instantly boosting your network’s total capacity and efficiency. It reduces problems like buffering and lag when the whole household is online.
How does MU-MIMO work?
MU-MIMO technology allows your router, which has multiple antennas, to manage several independent communication streams across the same Wi-Fi channel simultaneously.
Two technologies make this possible: spatial streams and beamforming.
- Spatial streams: Each antenna creates an independent channel to send data. For example, a 4x4 router can handle up to four parallel streams. It can dedicate all four to one powerful device, such as a gaming PC, or split them among multiple lower-power devices, such as smartphones.
- Beamforming: Instead of broadcasting signals everywhere, beamforming adjusts the phase and amplitude of signals from each antenna so they add up constructively toward the intended device, focusing energy and reducing interference.
Together, these technologies allow your router to handle multiple data streams efficiently, improving both speed and reliability across your network.
To better understand how routers, devices, and wireless signals work together, see our guide on network architecture.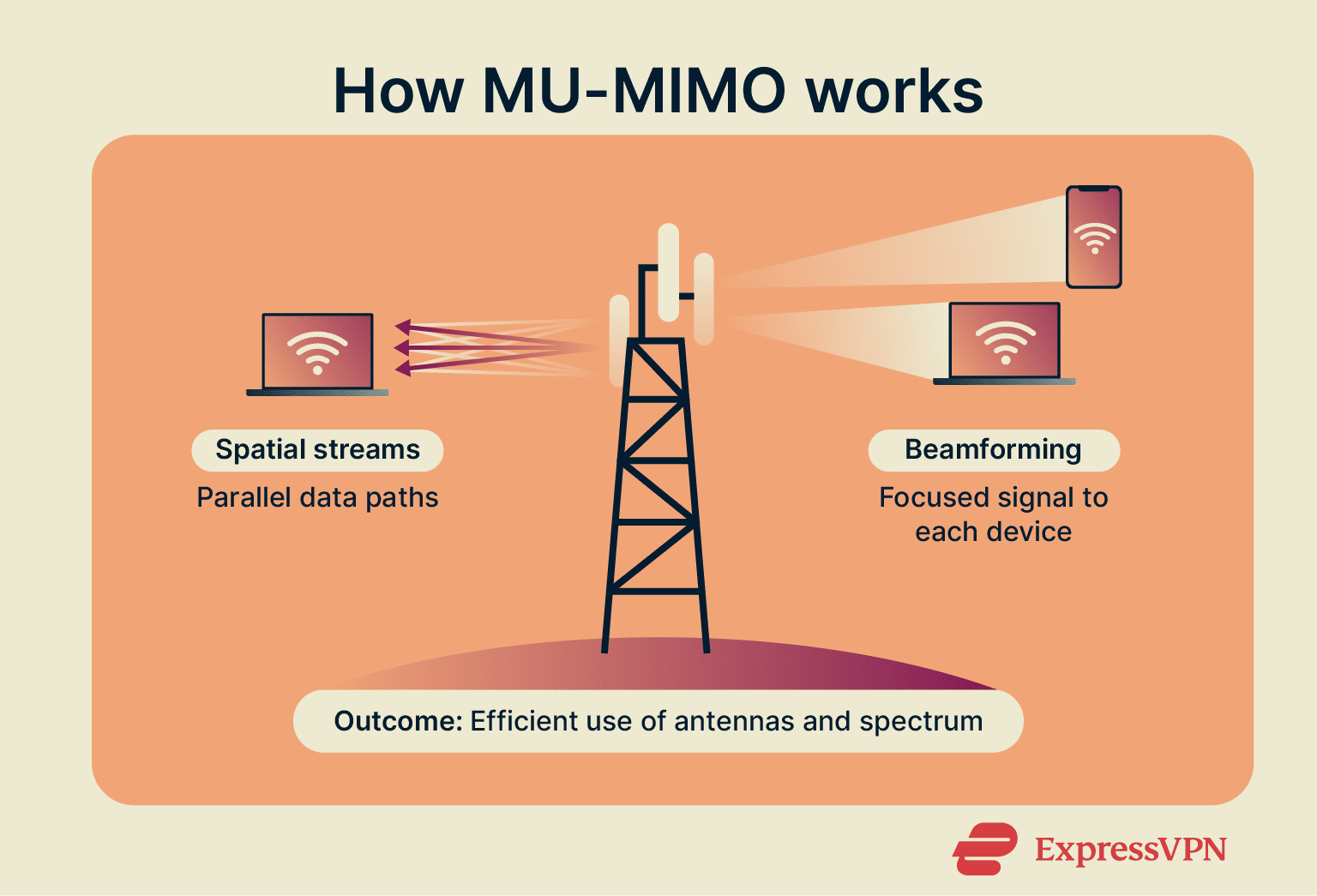
Key differences between MU-MIMO and SU-MIMO
To understand how MU-MIMO improves Wi-Fi efficiency, it helps to compare it with the older SU-MIMO standard. Here’s how they differ:
SU-MIMO:
- Sends data to one device at a time, even if multiple antennas are available.
- Devices take turns communicating with the router.
- Common in older Wi-Fi standards, such as Wi-Fi 4.
MU-MIMO:
- Sends data to multiple devices simultaneously, using different streams.
- Improves efficiency and reduces wait time on busy networks.
- Introduced in Wi-Fi 5 Wave 2 and enhanced in Wi-Fi 6.
MU-MIMO use cases
MU-MIMO shows its value when the network is busy. Here are some of the key places where MU-MIMO is used.
Home and smart home Wi-Fi networks
The modern home is the perfect place to see how important MU-MIMO really is. A single family can easily have 15 to 20 active devices running at once: phones, laptops, 4K streaming players, security cameras, smart speakers, and gaming consoles, for example.
In this busy home environment, MU-MIMO technology ensures:
- Less buffering: If one family member is streaming a 4K movie while another is on a work video conference, MU-MIMO makes sure both get their own high-speed connection. This significantly reduces buffering across the board.
- Better gaming: For gamers, MU-MIMO helps reduce lag (ping) by allowing the router to send game data to your PC or console without waiting for other devices to finish their downloads. This means more stable, lower-latency connections during gameplay.
- Smart device stability: Smart home gadgets (like cameras and thermostats) constantly send small packets of data. MU-MIMO is highly efficient at handling these tiny streams, preventing them from clogging the bandwidth needed for major tasks, like downloading a large file or backing up your laptop.
A stable network is the first step in a good security plan; make sure to also read up on how to secure your home Wi-Fi effectively.
Business networks
Small and medium-sized businesses typically have busy networks where consistent performance is key for productivity. While a small office’s network might have fewer users than a university’s, the demands are often higher due to mission-critical applications running simultaneously.
In business networks, MU-MIMO addresses the connectivity challenges related to modern collaboration tools:
- Video conferencing: Professional video platforms require extremely low network jitter and stable bidirectional data flow. MU-MIMO helps multiple employees join separate HD calls without degrading the overall quality.
- Mission-critical data transfers: Whether employees are uploading documents to a cloud server or backing up large files, MU-MIMO technology assigns independent streams. This prevents large transfers from slowing down the entire network while they’re in progress.
For managing visitor traffic, see our guide on setting up a Wi-Fi guest network to maintain security and performance segmentation.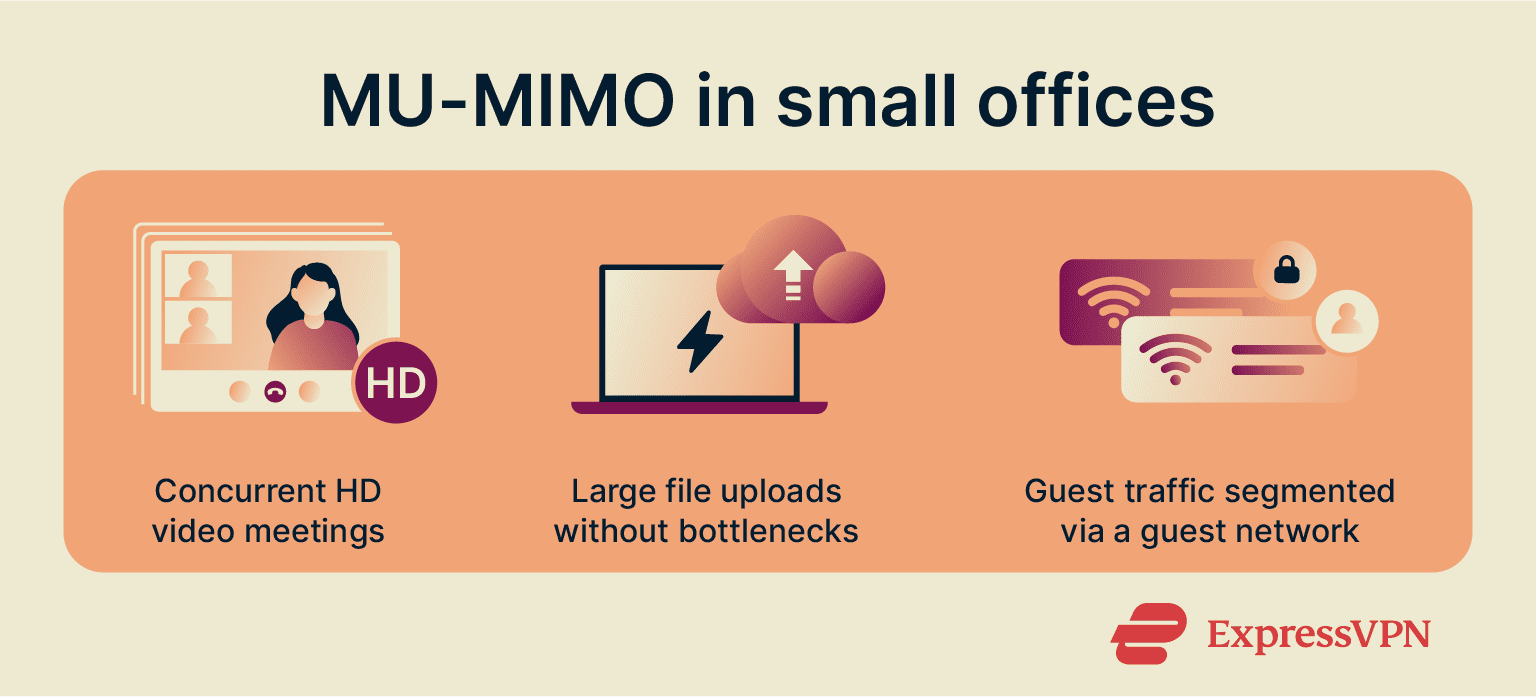
Public Wi-Fi hotspots
Busy public spaces like airport lounges, cafés, hotels, and convention centers often see a constant flow of new users and devices attempting to connect to open Wi-Fi networks. In these crowded settings, the goal isn’t top speed for any one user; it’s making sure as many users as possible can connect reliably and fairly, even if that means slightly slower speeds overall.
MU-MIMO helps by:
- Handling high volume: When high volumes of devices connect at once, traditional Wi-Fi quickly becomes unusable. MU-MIMO is important for allowing the access point to process dozens of requests simultaneously. This helps prevent overload when many users connect.
- Facilitating a consistent experience: MU-MIMO technology provides a much more consistent user experience, even if overall speeds aren't extremely fast. It reduces the slowdowns that occur when one user starts a large download by enabling the router to continue serving other devices without interruption.
Schools and universities
Educational institutions represent some of the most challenging high-density wireless environments. They typically see thousands of students and staff connect simultaneously for research, online learning, and administrative tasks.
Here’s how MU-MIMO helps enhance reliability in school and university networks:
- High user concurrency: During peak hours, traditional Wi-Fi networks would often fail as thousands of devices attempted to communicate at once. MU-MIMO technology allows access points to handle large volumes of concurrent data streams efficiently, preventing network failure in crowded digital classrooms.
- Stable environments for online tests: When entire libraries or classrooms are taking standardized digital tests simultaneously, consistent, low-latency connectivity is necessary. MU-MIMO helps reduce the connectivity spikes that could compromise test integrity.
- Fair access for all devices: MU-MIMO improves overall network efficiency by allowing multiple modern devices to transmit and receive data simultaneously. This reduces airtime contention, meaning even legacy Wi-Fi devices like older phones or tablets that only support SU-MIMO benefit indirectly. With less network congestion, these devices experience smoother and more consistent access.
MU-MIMO and VPN performance
A virtual private network (VPN) protects your online activity by encrypting your internet traffic and routing it through a secure server. This process adds a small amount of performance overhead, since your data travels farther and must be encrypted and decrypted along the way. The impact, however, depends heavily on the quality of the VPN’s infrastructure. Choosing a VPN with high-speed servers in many countries, like ExpressVPN, can help minimize slowdowns.
MU-MIMO doesn’t directly make your VPN faster, but it can improve your experience on busy Wi-Fi networks. By letting your router communicate with multiple devices simultaneously, MU-MIMO reduces local congestion and helps maintain steadier Wi-Fi performance, which indirectly keeps VPN connections smoother.
If you use a VPN directly on your router (either by installing a VPN on it or using one with built-in VPN protection like ExpressVPN Aircove), the router handles encryption and routes traffic for every connected device. MU-MIMO doesn’t speed up the VPN itself, but it helps the router share Wi-Fi more efficiently, keeping multiple devices stable even when they’re all using the VPN at once.
Streaming and gaming performance with MU-MIMO and VPN
When you’re gaming or streaming through a VPN, you want both speed and security. MU-MIMO can’t boost raw internet speeds, but it helps reduce local Wi-Fi congestion, making it easier to stay protected by a VPN without as much impact on quality or responsiveness, especially when several devices are active on the same network.
Benefits for home and business networks
The efficiency boost from MU-MIMO benefits both home users and small businesses that rely on VPN connections.
- At home: MU-MIMO helps keep Wi-Fi connections stable when multiple people are online. One person can stream securely through a VPN while others download updates or use cloud backups, with fewer slowdowns caused by Wi-Fi contention.
- At work: Employees using VPNs for video calls or accessing company resources benefit from MU-MIMO’s ability to handle multiple wireless devices efficiently. It doesn’t prioritize VPN traffic, but it helps maintain steady local Wi-Fi performance when several people share the same access point.
Types of MU-MIMO configurations
Not all MU-MIMO systems deliver the same level of performance, and the technology has improved with each new Wi-Fi generation. Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac) introduced downlink MU-MIMO, which allows the router to send data to multiple devices at once but not receive from them simultaneously.
Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) expanded on this by adding uplink MU-MIMO, so multiple devices can upload data to the router at the same time. It also increased the number of supported spatial streams, improving capacity.
A router’s MU-MIMO performance is shaped by two key factors: how many spatial streams it supports and whether it supports both downlink and uplink MU-MIMO.
2x2 vs. 4x4 vs. 8x8 MU-MIMO: Which is better?
These numbers show how many antennas and spatial streams a router can use to send and receive data at the same time. In other words, they indicate how many separate data streams can run in parallel to compatible devices (but that doesn’t mean one stream per device).
- 2x2 MU-MIMO: Uses two spatial streams. In practice, this can allow data to be sent to up to two compatible devices at once, though most client devices still use just a single stream.
- 4x4 MU-MIMO: Uses four spatial streams, helping routers manage traffic more efficiently when several devices are online. This setup is common in mid- to high-end home routers.
- 8x8 MU-MIMO: Uses eight spatial streams, usually found in high-performance or enterprise-grade Wi-Fi 6, 6E, and 7 routers. It can handle more devices in theory, but the benefit depends on how many of them actually support MU-MIMO and how much bandwidth is available.
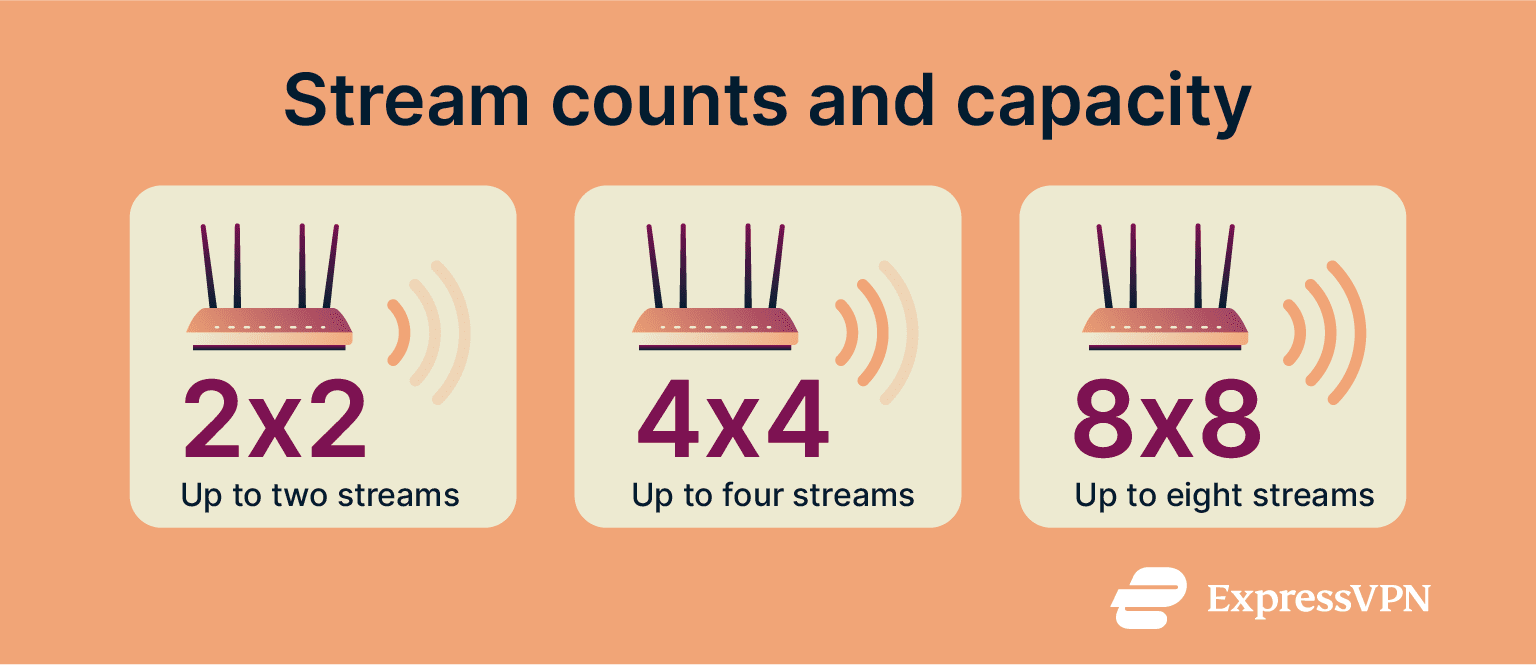
Downlink and uplink MU-MIMO
Another key factor affecting performance is the direction of the data stream. Previous Wi-Fi generations were mostly optimized for downloads, while modern applications depend on fast, reliable uploads as well.
The first version of MU-MIMO, downlink (DL) MU-MIMO, was introduced with Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac) Wave 2. It focused on improving traffic from the router to client devices, such as downloads and video streaming. This helps maintain consistent download speeds when retrieving data from a VPN server. However, older Wi-Fi 5 routers that only support DL MU-MIMO can experience upload congestion.
The major advancement came with Uplink (UL) MU-MIMO, introduced in Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax). This version optimizes data sent from devices back to the router, improving uploads, video calls, and in-game actions. For VPN users who frequently upload files, participate in video conferences, or play competitive online games, UL MU-MIMO helps to ensure outbound traffic remains smooth and responsive even when multiple devices are sending data at the same time. That said, support for uplink MU-MIMO is still expanding, and many client devices, such as laptops and smartphones, don’t yet take full advantage of it.
“Massive MU-MIMO” and Wi-Fi 6, 6E, and 7
The latest Wi-Fi standards have significantly improved MU-MIMO technology by increasing stream capacity and expanding available frequency bands.
- Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax): This standard introduced major upgrades, including optional uplink support and support for eight simultaneous streams. It often works in tandem with Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) to manage large numbers of connected devices more efficiently.
- Wi-Fi 6E and Wi-Fi 7: These newer generations keep the maximum number of MU-MIMO streams at eight but improve concurrency and throughput through wider channels and, in Wi-Fi 7, advanced features like Multi-Link Operation (MLO). Together, these upgrades make data transfers more efficient and help networks handle more simultaneous connections smoothly.
- Massive MU-MIMO: This term comes from 5G cellular networks and refers to systems that use dozens or even hundreds of antennas to serve many users simultaneously. It isn’t directly implemented in consumer Wi-Fi, but routers with 8×8 MU-MIMO borrow similar principles, bringing a level of parallel data handling once limited to enterprise networks into homes and small businesses.
MU-MIMO limitations and misconceptions
While MU-MIMO is an effective solution for boosting network capacity and stability, it's not the answer to every Wi-Fi problem. If users adopt the technology with unrealistic expectations, it can lead to frustration.
Even with the right setup, you might occasionally face connectivity interruptions that aren’t related to MU-MIMO itself. If that happens, see our guide on fixing ”no network connection” issues for troubleshooting steps.
Understanding these technical and hardware limitations is also part of keeping your network secure. Learn more about the standards that help keep Wi-Fi connections safe and reliable in our guide on network security standards.
Potential drawbacks of MU-MIMO technology
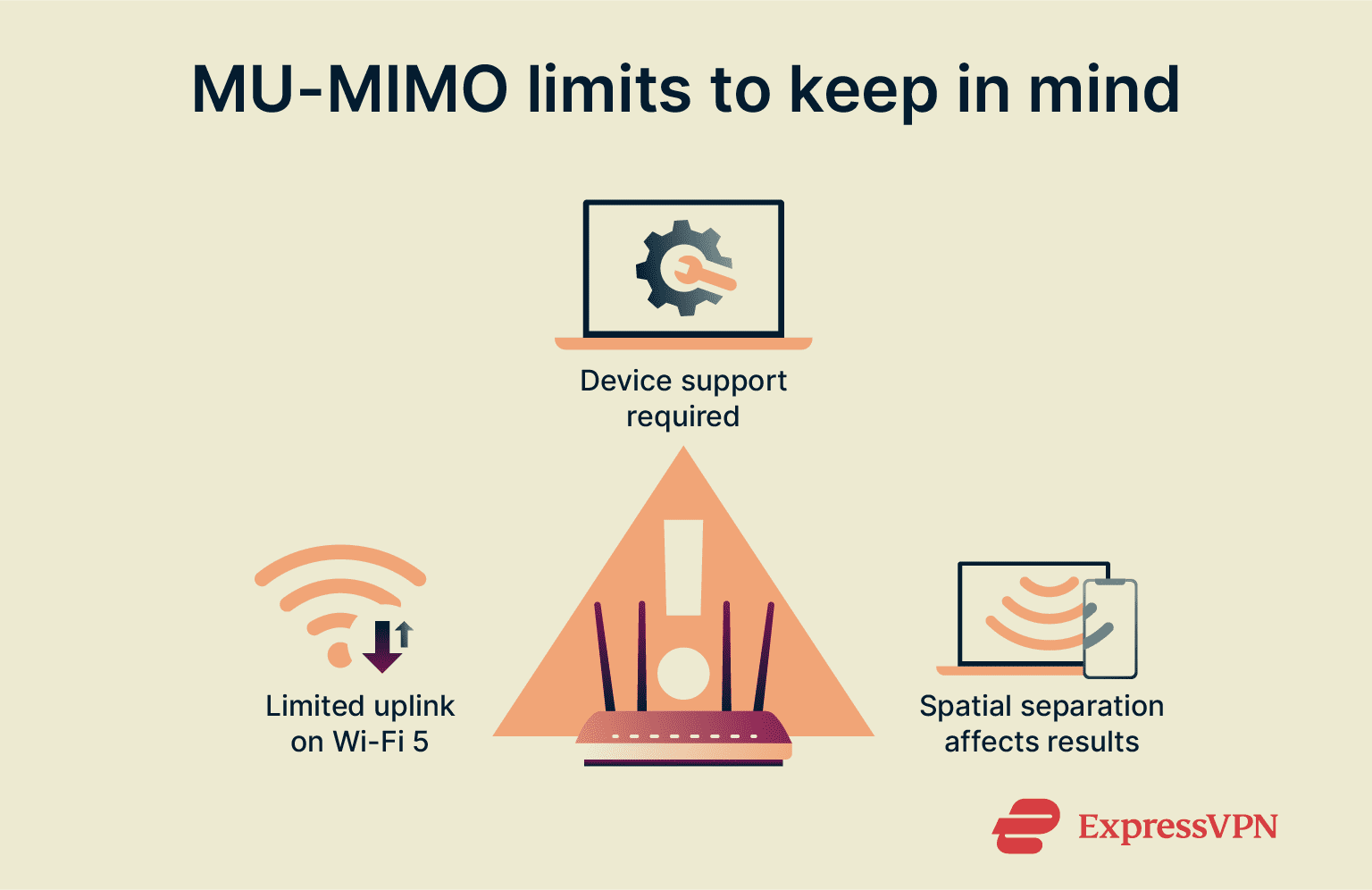
While MU-MIMO is highly effective at improving network capacity, several technical factors can limit the performance gains you see, especially in home environments.
- Client compatibility is required: For MU-MIMO to work, both the router and the client device (such as a laptop or smartphone) must support the technology. If an older or non-compatible device connects to an MU-MIMO router, that connection automatically reverts to the older, slower SU-MIMO method.
- Limited uplink support in Wi-Fi 5: If you’re using a Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac Wave 2) router, MU-MIMO only works for downloads. Uploads remain prone to congestion, which can impact two-way communication tools like video conferencing.
- Spatial separation matters: The beamforming technology that supports MU-MIMO requires devices to be physically separated. If multiple devices are clustered close together, the router may struggle to isolate their individual data streams, reducing the overall efficiency gains. That said, there are some new strategies being developed to address this, so it might be less of an issue in the future.
Common misunderstandings
A common misconception is that MU-MIMO directly increases internet speed or dramatically boosts VPN performance. In reality, its benefits are more specific and limited than that:
- It doesn’t increase your internet service provider (ISP) speed: If your internet plan offers 100 Mbps, MU-MIMO won’t make it faster. It only optimizes how existing bandwidth is shared among multiple devices.
- It doesn’t override VPN protocol limits: MU-MIMO doesn’t make a VPN encrypt or transmit data any faster. Using an efficient VPN protocol (like Lightway or WireGuard) can still improve overall VPN stability and performance, but MU-MIMO only helps the Wi-Fi portion of the connection.
Router and VPN service compatibility issues
Even with compatible clients and an MU-MIMO router, certain operational factors can still affect VPN performance. Not all MU-MIMO routers can run a full VPN client natively, and your router’s firmware must fully support the VPN protocol you want to use. You can consult the official documentation to confirm whether your router supports full VPN functionality.
Implementation quality also matters. In some routers, MU-MIMO may be disabled by default, or the firmware may occasionally revert to SU-MIMO mode. Keeping router firmware updated helps prevent these issues and sustain network reliability in the long term.
Some routers also maintain detailed traffic logs, which can add unnecessary latency and affect VPN speed. For both privacy and performance, it’s important to understand what Wi-Fi router logging is and how to manage it effectively.
FAQ: Common questions about MU-MIMO
Does MU-MIMO really boost VPN speeds?
Not directly. Multi-User, Multiple-Input, Multiple-Output (MU-MIMO) doesn’t increase your internet speed or VPN encryption rate. It improves the reliability of your Wi-FI connection by reducing local network congestion, which can in turn help your VPN traffic stay smooth.
Do all routers support MU-MIMO and VPN at the same time?
No. Most modern high-end routers support Multi-User, Multiple-Input, Multiple-Output (MU-MIMO), particularly Wi-Fi 6 models, but only some can run a full VPN client natively. Compatibility between the router’s firmware and the chosen VPN protocol, such as Lightway or WireGuard, is essential.
How many devices can benefit from MU-MIMO with VPN?
The number of devices Multi-User, Multiple-Input, Multiple-Output (MU-MIMO) can support at the same time isn’t affected by whether they’re using a VPN. It depends on how many spatial streams your router supports and how many of those your connected devices can use. For example, a 4x4 MU-MIMO router can theoretically serve up to four single-stream devices simultaneously, but actual performance depends on how the router groups devices and their capabilities.
Is MU-MIMO worth it for VPN users?
Yes. In multi-device households or environments that use bandwidth-heavy applications such as 4K streaming and gaming, Multi-User, Multiple-Input, Multiple-Output (MU-MIMO) can significantly improve stability and reduce latency on a Wi-Fi-connected device. This helps eliminate lag spikes and connection drops that can occur when encrypted VPN traffic competes with other network activity.
Take the first step to protect yourself online. Try ExpressVPN risk-free.
Get ExpressVPN