What does jailbreaking an iPhone do? Is it worth the risk?

You may have heard about people jailbreaking their iPhones to install unauthorized apps or customize the operating system in ways Apple doesn’t allow.
While it can give you more control over your device, jailbreaking also comes with serious risks, like voiding your warranty or even rendering your iPhone unusable.
This guide explains what jailbreaking involves, weighs the pros and cons, and helps you decide whether it’s ever worth the risk.
What is jailbreaking an iPhone?
Jailbreaking an iPhone means removing the built-in software restrictions that Apple puts in place on iOS devices. Think of it as gaining “admin rights” to your phone. Once you jailbreak it, you can customize your device, install apps and tweaks that Apple normally doesn’t allow, and basically take full control of the system.
Just a heads-up: jailbreaking removes many of Apple’s built-in security protections, which can leave your phone more vulnerable to malware, crashes, and data loss. Since it weakens your phone’s defenses, it’s not something we recommend, especially if you rely on your iPhone for important things.
How jailbreaking works on iOS
The process itself depends on your iPhone model and which version of iOS you’re running. Usually, you use a jailbreak tool that does most of the work for you, like applying a kernel patch behind the scenes to give you full access.
Some of the common jailbreaking tools include:
- Checkra1n
- Unc0ver
- Taurine
- Dopamine
- Palera1n
- XinaA15
- NathanLR
- Meowbrek2
Jailbreaking vs. unlocking: What’s the difference?
People often confuse jailbreaking with unlocking, but they’re quite different. Unlocking a phone is all about removing restrictions from your carrier. For example, if your iPhone is locked to Sprint, it won’t work with a SIM card from another network. Unlocking it lets you use it with any carrier, anywhere in the world. You can contact your carrier to request an iPhone unlock. As long as your account is in good standing, it shouldn’t be an issue.
Unlocking a phone is all about removing restrictions from your carrier. For example, if your iPhone is locked to Sprint, it won’t work with a SIM card from another network. Unlocking it lets you use it with any carrier, anywhere in the world. You can contact your carrier to request an iPhone unlock. As long as your account is in good standing, it shouldn’t be an issue.
Jailbreaking, on the other hand, is about removing Apple’s software restrictions. It gives you more control over the device so you can install custom themes, tweaks, or apps that aren’t available on the App Store. But it also comes with bigger risks, like security vulnerabilities or legal gray areas, depending on what you install and where you live.
Jailbreaking vs. rooting (iOS vs. Android)
Jailbreaking and rooting both give users more control over their devices, but they apply to different systems. Jailbreaking is for Apple devices, while rooting is the Android version of the same idea. Both let you access deeper parts of the operating system, but the tools and risks involved depend on the platform you're using.
Is jailbreaking still possible today?
Yes, jailbreaking is still possible, but it’s not nearly as common or straightforward as it used to be. Apple regularly pushes security updates to close off vulnerabilities, making jailbreaking more difficult with each release. The company also publishes warnings about the risks and strongly discourages users from tampering with iOS.
Because of that, many feel jailbreaking is slowly fading out, and newer iOS versions may eventually become nearly impossible to break into.
That shift is also happening because the need to jailbreak is shrinking in some regions. In the EU, for example, Apple has started allowing third-party app stores under the Digital Markets Act (DMA). That means users in Europe can install apps outside the App Store without jailbreaking, which was once a major reason to do it.
Outside the EU, however, Apple’s restrictions still apply, so while jailbreaks are becoming rarer, they’re not gone just yet.
Types of jailbreaking
There are a few different types of jailbreaks out there, each with its own pros, cons, and level of convenience.
Tethered jailbreak
A tethered jailbreak only works until you turn your device off. If your phone dies or restarts, it won’t fully boot on its own; you’ll need to connect it to a computer and run the jailbreak tool again every time your device reboots to get it working properly.
Without doing this, the device might freeze on the Apple logo, enter Recovery Mode, or start up without any jailbreak features. Cydia and other jailbreak apps may crash, and custom tweaks won’t work. The good news is that any changes you made (like installed apps or settings) will still be there. You just need to "boot tethered" with a computer to activate them again.
Tethered jailbreaks were more common on older iPhones and iPods that used hardware-level exploits Apple couldn’t fix with software updates. They’re rarely used today because they’re inconvenient, and newer devices are harder to jailbreak this way.
Untethered jailbreak
An untethered jailbreak is the most user-friendly. Once installed, it remains in effect even after rebooting. You can power off or restart your device, and it will remain jailbroken. (Note: Updating iOS usually removes the jailbreak.)
Semi-tethered jailbreak
With a semi-tethered jailbreak, you can turn your device back on without help from a computer, but it will boot into a non-jailbroken state. To regain jailbreak features, you’ll need to reconnect to a computer and rerun the jailbreak tool.
Semi-untethered jailbreak
A semi-untethered jailbreak lets your device reboot on its own, but it won’t stay jailbroken after a restart. That’s because it boots into its normal state. To bring jailbreak features back, you just run a special app on the device; no computer is needed. This method has become the most common because it’s easy and flexible.
Which type is right for me?
To be honest, none of them is risk-free. We don’t recommend jailbreaking in any form due to the potential risks, including security issues, instability, and the possibility of bricking your device.
If you're still thinking about it, do your research and make sure you understand what you're getting into. There’s no completely safe or guaranteed way to jailbreak an iPhone.
How to tell if an iPhone has been jailbroken
If you’re buying or inheriting a used iPhone, it’s a smart idea to check whether it’s been jailbroken. A jailbroken device can behave differently and may even pose security risks. Here are a few signs to look out for:
Signs in the Settings app
While you won’t find a big “This device is jailbroken” warning in Settings, there are a few subtle clues.
- Open the Settings app on your iPhone and tap on General.
- Tap on VPN & Device Management (or Profiles & Device Management on older devices).
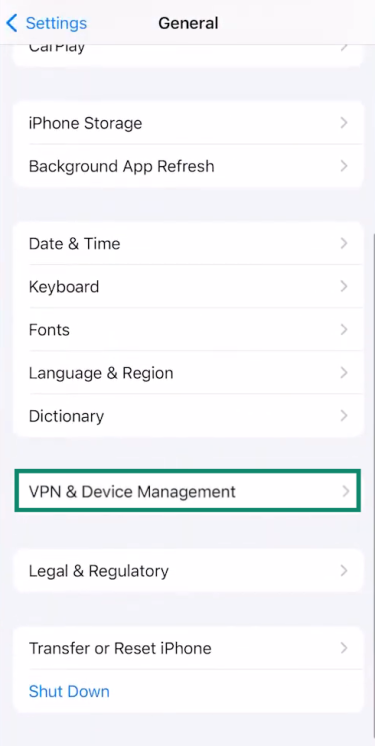
If you see any strange or unfamiliar profiles installed on that page, especially ones related to jailbreak tools or unofficial apps, that’s a red flag. Some jailbreak tweaks may also add custom settings menus or options that wouldn’t normally appear on a stock iPhone.
Suspicious apps or icons
Jailbroken iPhones often have unsigned apps that don’t come from the App Store. Keep an eye out for tools like Cydia, Sileo, Zebra, or Installer 5; these are alternative app stores or package managers used in jailbroken environments. You can search for them by swiping down on the home screen and typing the names.
Performance, crash, or battery issues
A jailbroken iPhone might behave oddly. You could notice random crashes, lag, or unusually fast battery drain due to background tweaks or poorly optimized apps. That said, these symptoms aren’t exclusive to jailbreaking; they could also be caused by age, malware, or buggy updates. But when paired with other signs, they’re worth taking seriously.
Some performance problems, like storage issues, may not be related to jailbreaking and could be resolved if you clear system data on your iPhone. Alternatively, battery problems might be addressed through simple tweaks to improve battery life.
Using tools to detect jailbreaking
For a more reliable check, try a mobile security app that scans your iPhone for signs of tampering and can alert you if it finds evidence of jailbreaking.
Pros of jailbreaking an iPhone
Jailbreaking isn’t without its risks, and we definitely don’t recommend it. However, some users still do it to unlock more control and flexibility.
Here’s what draws people in:
- More control over your iOS device and apps: Jailbreaking gives you root access, which lets you change system settings and install apps Apple doesn’t approve. That includes third-party or modified apps not found in the App Store, some of which offer features blocked by Apple or ones that aren't available in your region (though there are official ways to change your App Store country without jailbreaking).
- Customization: From custom icons and themes to new fonts, sounds, and gestures, jailbreaking lets you personalize your iPhone way beyond what Apple allows. You can redesign your home screen layout, add widgets in new places, or change how menus and animations behave.
- Removing Apple bloatware: Certain Apple apps like Health and Messages can’t be deleted; you can only hide them. If you use an older OS version, the list of unremovable apps is longer. Jailbreaking gives you the option to remove any app you want, freeing up space and decluttering your device.
- Unlocking hidden features: Jailbreaking can enable features Apple doesn’t officially support, like split-screen multitasking. These kinds of tweaks can significantly change how your device works.
Cons and risks of jailbreaking
While jailbreaking might sound appealing for the extra control, it comes with real risks, and for most users, those risks outweigh the benefits. Here’s what you need to know:
Here’s what you need to know:
- You might lose Apple support: Apple strongly discourages jailbreaking, and while it doesn’t automatically void your entire warranty, it can make things tricky. If you bring in a jailbroken device for repair, Apple can refuse service, especially if the issue is linked to the jailbreak. Even if the warranty is still valid, support may be limited until you remove the jailbreak (if possible).
- No more automatic updates: Jailbreaking can interfere with iOS updates. Many jailbreak tools block over-the-air (OTA) updates by default to prevent breaking the jailbreak. That means you might miss out on important security patches or new features unless you manually restore your phone.
- Higher risk of malware, spyware, and data breaches: Jailbreaking removes many of Apple’s built-in security protections, leaving your device more exposed. Third-party apps from unofficial sources may contain hidden malware or spyware, and without App Store vetting or regular iOS patches, the risk of data theft, remote access, and privacy breaches goes up significantly.
- Frequent crashes and app instability: Modifying system files and adding custom iOS tweaks can make your device unstable. You might run into random crashes, slower performance, or apps that simply stop working. Even apps you use every day, like your banking app or mobile games, can behave unpredictably or crash on launch.
- Apple services might not work properly: Features like iCloud, Apple Pay, FaceTime, or iMessage may not function as expected on a jailbroken device. You might experience sync issues, connection failures, or random bugs depending on your iOS version, the jailbreak used, and any system tweaks you’ve applied.
- Risk of bricking your device: A botched jailbreak or an incompatible tweak can leave your device stuck in a boot loop or completely unresponsive. In tech terms, this is called bricking your phone. While some issues can be fixed with a full restore, in other cases you might need professional repair or a new device altogether.
- Some apps may stop working or ban jailbroken devices: Many popular apps, especially banking, finance, and streaming services, check for jailbreaks and block access if one is detected. In some cases, your account might even get flagged or banned.
Is jailbreaking an iPhone legal?
In most places, jailbreaking isn’t illegal. Still, it can land you in legally murky territory, depending on how you use your jailbroken device.
U.S. legal status
In the United States, jailbreaking a phone is legal under exemptions to the Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA). These exemptions have been in place since 2010 for smartphones and since 2015 for tablets and smartwatches.
However, that doesn’t mean anything goes; using your jailbroken device to access pirated content, bypass copyright protections, or install illegal apps is still against the law.
Other countries
Jailbreaking is generally legal in many countries, including most of Europe, India, and New Zealand, but the legal framework isn’t always as clearly defined as it is in the U.S.
For example, the EU Copyright Directive prohibits bypassing DRM (Digital Rights Management), but national laws vary. Some countries allow limited personal-use modifications, while others interpret DRM circumvention more strictly.
In Australia, jailbreaking exists in a legal gray area. The law prohibits bypassing copyright protection systems unless it's for very specific purposes permitted under section 116AN of the Australian Copyright Act 1968, and general personal use isn’t clearly exempted.
Jailbreaking isn’t explicitly illegal in Singapore, but because it involves breaking access control measures protected under section 425 of the Copyright Act 2021, it’s effectively prohibited unless one fits into a very narrow, statutory exception.
How to reverse jailbreaking or fix a jailbroken iPhone
If you've got a jailbroken iPhone and want to undo it, whether for security, stability, or to get Apple support again, there are a few reliable ways to return your device to its original state.
1. Back up before you begin
Restoring your device usually means wiping everything. So before you start, back up your iPhone. This ensures you don’t lose any important photos, messages, or files during the reset.
Note: iCloud or Finder/iTunes backups don’t preserve the jailbreak or its tweaks, but they can include leftover settings or preference files from those tweaks. While this doesn’t usually cause issues, some users have reported that restoring these settings to a non-jailbroken device may lead to minor glitches or inconsistencies. To ensure a completely clean slate, consider setting up your iPhone as new after restoring, but keep in mind this won’t recover your previous data, apps, or settings.
How to back up your iPhone via iCloud
- Open the Settings on your iPhone and tap on your profile at the top of the screen.
- Tap on iCloud.
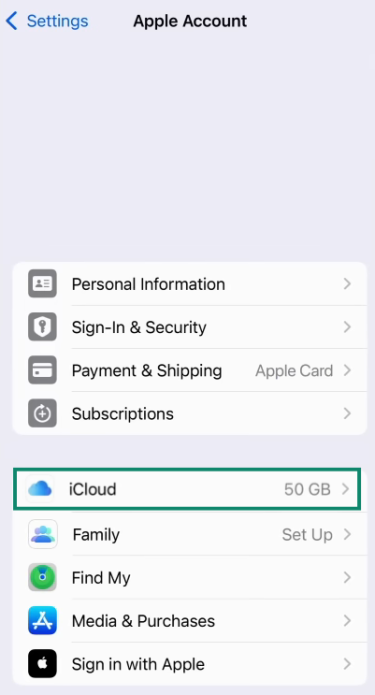
- Tap iCloud Backup.
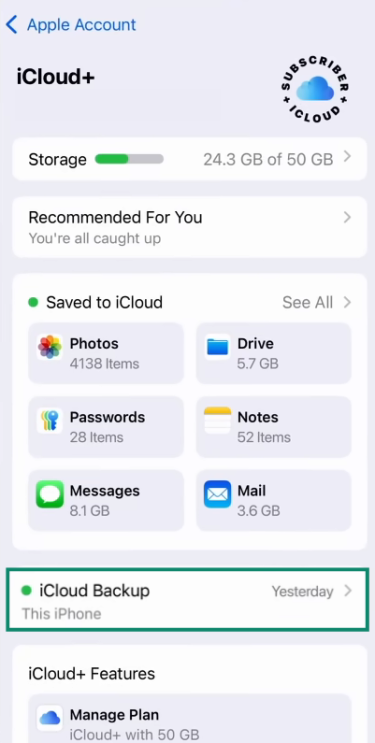
- Make sure the Back Up This iPhone option is toggled on. Press Back Up Now to create a backup.
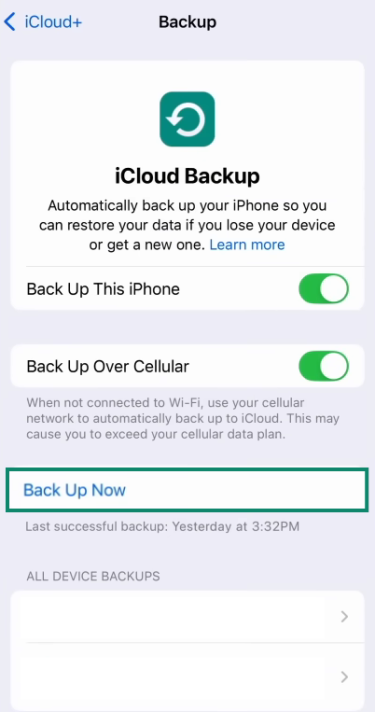
How to back up your iPhone through Finder
To back up your iPhone using Finder, you’ll need macOS 10.15 (Catalina) or later.
- Connect your iPhone to your computer and open a Finder window. Click on your iPhone name, which should appear in the sidebar under Locations.
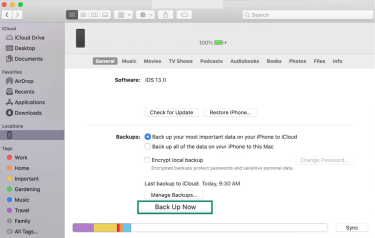
- Go to General, select Back up all of the data on your iPhone to this Mac, and click Back Up Now.
How to back up your phone using iTunes
Apple replaced iTunes with Finder on Macs starting with macOS Catalina (10.15), but iTunes is still used on Windows PCs and older Macs (macOS Mojave or earlier). If you’re using one of those systems, follow these steps:
- Open iTunes and connect your iPhone to your computer.
- Click the device icon.
- Under the Summary tab, select Back Up Now to create a local backup.
- To encrypt your backup, check Encrypt local backup.
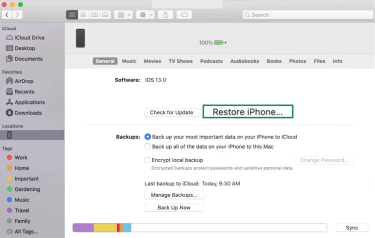
2. Restore via iTunes or Finder
The most common method is using iTunes (on Windows or older macOS versions) or Finder (on newer Macs).
- Connect your iPhone to your computer. Open Finder and click on your device in the sidebar on the left.

- Click on the Restore iPhone button, then follow the on-screen instructions.
3. Use DFU mode for full reset
If a regular restore doesn’t work or your device is stuck, Device Firmware Update (DFU) mode can help. It lets you wipe and reinstall iOS from scratch.
If your device has a Home button:
- Press and hold both the Power and Home buttons at the same time.
- Keep holding both for 3 seconds after the screen goes black.
- Release Power but keep holding Home until Finder/iTunes detects the device.
If your device doesn’t have a Home button:
- Press and hold the Power button.
- Wait for 3 seconds, then press press and hold the Volume Down button. Continue holding the Power button.
- Hold both buttons for 10 seconds, then release the Power button.
- Hold the Volume Down button for 5 more seconds.
- Release when Finder/iTunes detects the device.
Once in DFU mode, you can follow the same restore process as above.
When to ask for expert help
If you’re not confident doing it yourself, it’s best to get help, but keep in mind that Apple may refuse support for jailbroken devices. In that case, you should reach out to a trusted third-party technician or repair service with experience in restoring iPhones. They can help you back up your data and safely return the device to its original state—no stress, no guesswork.
Safer alternatives to jailbreaking
You don’t have to jailbreak your iPhone to make it more useful or personal. Apple has gradually opened up iOS to allow for more customization and control without the risks of jailbreaking. Here are some safer ways to enhance your device.
Use shortcuts and automations
Apple’s Shortcuts app is a powerful tool that lets you create custom routines, quick actions, and automations. Whether it's launching multiple apps with a single tap, organizing your reminders, or setting up time-based triggers, you can seriously boost productivity without touching the system code.
Try Safari extensions and App Library hacks
Apple’s Safari browser supports a range of extensions to enhance its functionality, improve privacy, and introduce new features. This gives you ways to customize your device safely. The App Library, too, lets you organize your apps, create hidden folders, or implement custom layouts to suit your preferences.
Wait for official iOS updates
Many of the features people once jailbroke their phones for, like screen recording, custom widgets, or Dark Mode, are now part of iOS. Apple continues to roll out new features with each update, so if you're waiting on something specific, it's often worth holding off to see if it becomes official.
Participate in Apple’s feedback channels
Got a feature idea or improvement in mind? Head to Apple’s Product Feedback page and share your thoughts. Apple has added popular features in the past thanks to user input—so you never know: your suggestion could shape the next version of iOS.
How to stay safe with a jailbroken iPhone
If you decide to jailbreak your iPhone despite the risks, it’s important to take extra steps to protect your device and data. With a bit of caution, you can reduce the chances of things going wrong.
Use only trusted jailbreak repositories
There are many jailbreak tools and repositories, and some have better reputations than others. Stick to using the most trusted and widely recommended ones.
Engage with communities like r/jailbreak on Reddit, where users often share experiences and warn about malicious repositories. Also, platforms like TweakReviewsDB offer user-submitted reviews and compatibility information for various tweaks, helping you make informed decisions.
Install a firewall app or VPN
Firewalls and VPN apps can help reduce some of the risks that come with using a jailbroken device. A VPN, for example, encrypts your internet traffic, making it harder for trackers or malicious actors to snoop on your activity.
Setting a VPN up on an iPhone is straightforward and doesn’t require altering the system. If needed, you can just as easily turn off your VPN when it's not required.
When you jailbreak your iPhone, you gain the ability to install firewall apps that provide granular control over your device's network activity. They can monitor and manage outgoing connections, allowing you to permit or deny internet access for individual apps. This level of control can help prevent unauthorized data transmission and enhance your privacy.
Regularly check for malware or spyware
Usually, iOS doesn’t let antivirus apps run full system scans. Apple locks down system access to keep things secure, which means traditional anti-malware tools don’t really work.
But if your iPhone is jailbroken, those restrictions are gone. That opens the door for tools apps that can check for sketchy tweaks or known malware hiding in the system.
Back up often and monitor unusual behavior
Create backups regularly, especially before installing anything new. That way, if something goes wrong (like crashing, lag, or weird behavior), you can roll back to a stable version of your system. Keep an eye out for signs like overheating, unusual pop-ups, or sudden battery drain—these could indicate trouble.
If something seems off, remove the most recent tweak or app. If problems persist, restore from a backup or do a full reset if needed.
FAQ: Common questions about jailbreaking an iPhone
Can Apple tell if I jailbreak my iPhone?
Apple can detect if an iPhone has been jailbroken, especially if you bring it in for repair. Technicians are trained to spot the signs, whether it's through system diagnostics or visible changes to the device. However, Apple doesn’t actively scan devices remotely for jailbreaks, so they won’t know unless the phone is physically inspected.
Some apps, like banking or streaming services, might stop working if they detect a jailbreak, but that happens on the app’s side, not because Apple is monitoring your device.
Why is Apple so against jailbreaking?
Apple’s goal is to keep iPhones secure, stable, and running the way they were designed to. Jailbreaking bypasses those built-in protections, letting users install apps or make changes that haven’t been reviewed for safety or compatibility. From Apple’s perspective, that opens the door to bugs, crashes, and security risks—things the company works hard to prevent.
What does jailbreaking an iPhone actually do?
Jailbreaking removes Apple’s built-in software restrictions and gives you root access (basically full control over the device). This lets you do things Apple normally doesn’t allow, like installing unofficial apps, changing how the system looks and behaves, or tweaking core features to suit your preferences.
Can I still use banking or payment apps after jailbreaking an iPhone?
You might be able to use some banking or payment apps, but many of them are designed to detect jailbroken devices and will block access for security reasons.
Is jailbreaking even worth it today?
For most people, jailbreaking isn’t worth it. The risks, like security issues, app blocks, and system instability, far outweigh the benefits.
Are jailbroken iPhones illegal?
It depends on your location and the laws in your area. Jailbreaking iPhones is not illegal in the U.S., U.K., and various other countries, but you can still face legal trouble if you engage in any illegal activities on a jailbroken phone, like copyright infringement.
Does jailbreak make an iPhone faster?
Not by default. While some tweaks claim to speed things up, jailbreaking also opens the door to instability, crashes, and lag.
Will I lose data if I jailbreak my iPhone?
There’s definitely a risk. You may lose access to certain apps and accounts, and your phone will be at greater risk of malware infections, hacking, and data breaches, since you won’t receive important security patches from Apple.
Is jailbreaking my phone legal?
In the U.S., yes, jailbreaking a phone is legal. It’s also legal in many other countries, including much of Europe. However, laws vary by region, and in some places, the legal status is unclear or restricted. Always check your local laws before proceeding.
What is the jailbreak app on the iPhone?
There’s no official “jailbreak app” that comes with iPhones. Instead, jailbreaking is done using third-party tools. Once jailbroken, your iPhone may have a new app like Cydia or Sileo, which acts as an alternative app store for downloading tweaks, themes, and unofficial apps.
Take the first step to protect yourself online. Try ExpressVPN risk-free.
Get ExpressVPN






Comments
great!!!
I have to disagree. Considering that, especially in the Android segment, manufacturers have been slow about pushiung updates and havent been doing really do a lot of them either, a custom rom and/or a root may actually make it MORE secure, you just need to know what you are doing. for example, you might be able to get yourself a permanent root and that use that to fix the hole that gave you root in the first place. also at least on android, root usually comes with a root manager like SuperSU or Superuser, which means apps have to request root AND get approval by the user. root/Jailbreak is basically just another facet of the right to repair, but on the software side.
Please remove this article and educate yourself on what rooting and jailbreaking actually is.
Add me to the list of people who strongly disagree with you. Choosing to install an alternative OS is good. Accepting the spyware and bloatware you know is already installed on your device because you might be at risk later is silly. Saying anyone who disagrees with you is not sane is just insulting.
A very misleading article. You seriously think an aging phone that no longer receives official updates is going to be more secure left as it is rather than rooting and updating it yourself.
I disagree. Once the hacking communities really started picking up and noticing hardware limitations set by oem's, thousands of people were abel to develop better operating systems with better security features than apple or microsoft or linux, programmed themselves on their devices. Jailbreaking and rooting devices, especially when youre doing it to look at security flaws, is actually VERY important. Trusting the oem's isnt a good idea all the time for many reasons. One of the reasons for many restrictions on software that you use on your hardware, is having to pay to use a feature, which you can get for free with a custom OS. Making sure people jailbreak and root their devices to look at security flaws and understand how they work would make people more secure in the long run. Even with black hat hackers. IOS is the PRIME example of this. People had to break the security of the iphone to jailbreak it and guess what? Not only did it prompt apple to make more secure software, but it also prompted developers to make security measures FOR jailbroken and rooted devices. You guys are too close minded on jailbreaking and security. I can understand if youre not a developer and dont code, you probably should learn a thing or two before deciding on jailbreaking. However for the people who are in this scene and have seen how jailbreaking has affected devices and companies, we KNOW you are wrong. Developers for jailbreaks dont want to just pirate games and apps. We want to make our phones genuinely better than the oem made it to be. Even with security.
This is not true at all. How about you do your research first instead of making all these BS claims.
This whole article is complete Rubbish with a big R. Please either correct all the info in this very misleading piece of writing or better yet, delete it asap! And for the future, check your facts more thoroughly next time.
Want to learn more about
I'm concerned now on how or why your even detecting if a device is jailbreaking or rooted. Did they get to yall? Are the power that be got to yall and now bout to start logging as well like they tried to make yall do in India? Starting to worry about yall. Especially when I heard yall were considering ExpressVPN come attach to Windows? Yeah. Dont risk ya biz like that. Stay away from anything associated with BG would be my advice.