How to check your internet connection

Whether your Wi-Fi won’t connect, speeds feel sluggish, or your connection keeps dropping, the first step to fixing the problem is understanding the root cause.
This guide covers how to check your internet connection on your desktop and smartphone. We also show you how to test your internet speed using online tools and troubleshoot common connection problems.
How to check if your Wi-Fi is working
Here’s how you can check your Wi-Fi connection status on Windows, Mac, Android, and iOS devices.
Check your internet connection on Windows
Here are three ways to check your internet connection on a Windows device.
- Check the network icon in the taskbar.
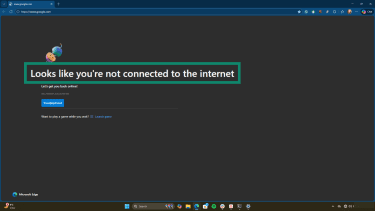
- Open a web browser and try to load a website. If you're not connected, you’ll get a message like this:
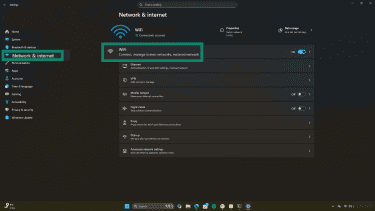
- Open Settings, select Network and Internet, and check the connection status.
Check your internet connection on macOS
Here are several ways to check your internet connection on a Mac device.
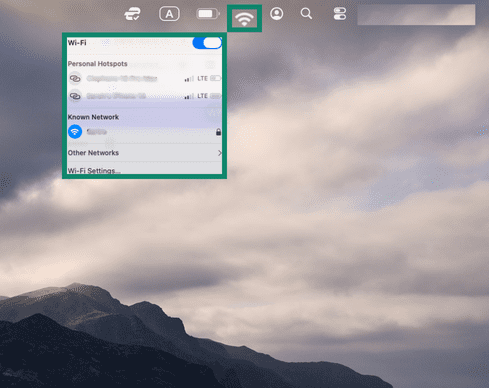
- Click the Wi-Fi icon in the menu bar. The Wi-Fi symbol next to the network you’re connected to will be blue.
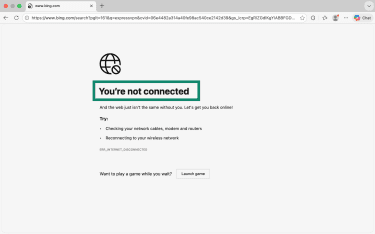
- Open a web browser and try loading a website. If you're not connected, you’ll see a notice along these lines.
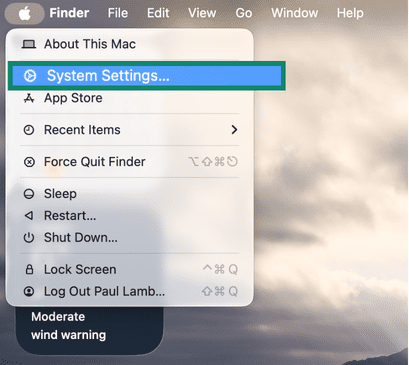
You can also check your internet connection status via System Settings. Here’s how:
- Open System Settings. It might also be labeled System Preferences if you’re using an older version of macOS.
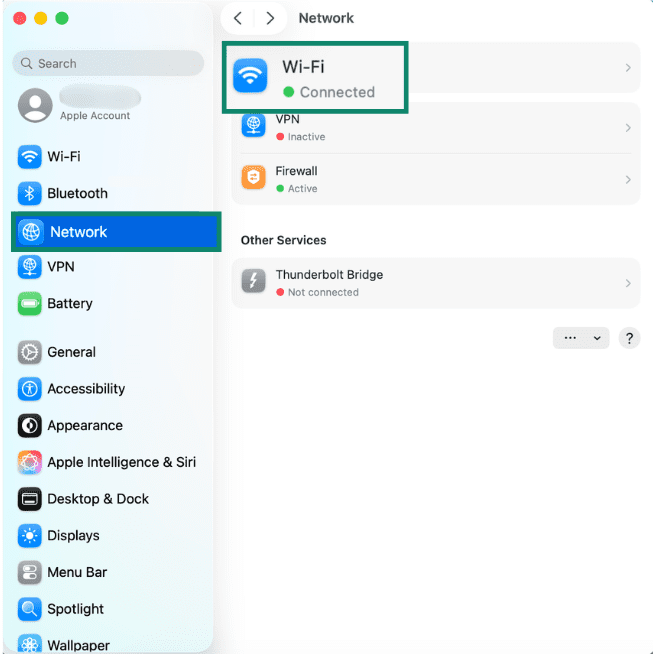
- Select Network. You’ll then see the connection status.
Check your internet connection on Android
Checking your internet connection on Android depends on whether you’re using Wi-Fi or mobile data. Note that the labels for these steps may vary slightly depending on the operating system.
Here’s how to check if you’re connected to Wi-Fi.
- Click the settings icon in your app library.

- Select Connections.
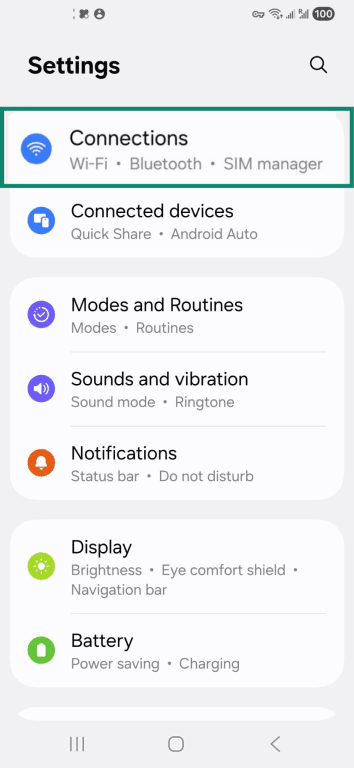
- Under Wi-Fi, it will either show the name of the Wi-Fi network you’re connected to or indicate you aren’t connected.
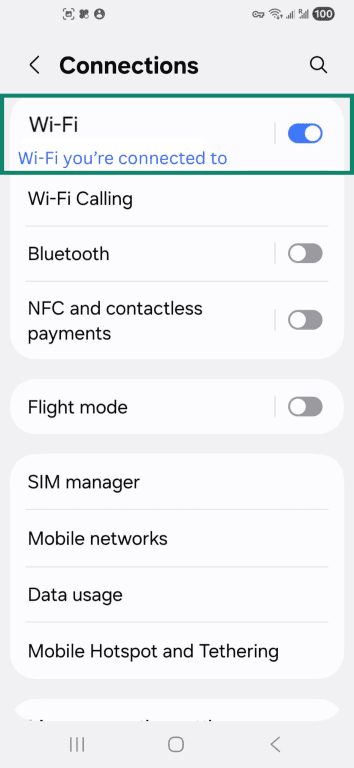
Here's how to check if your mobile data is working:
- Click the Settings icon in your app library.

- Select Connections and turn Wi-Fi off. Then tap Mobile networks.
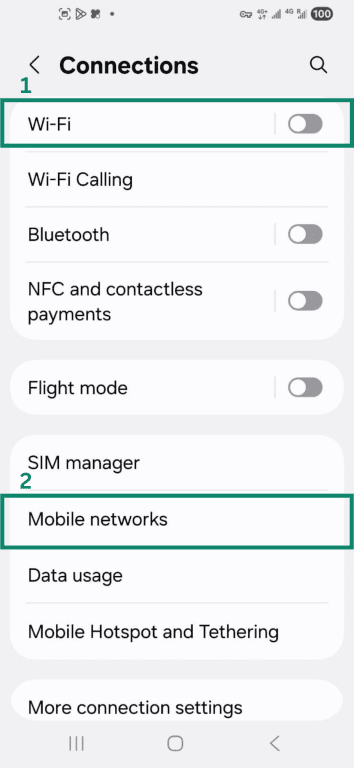
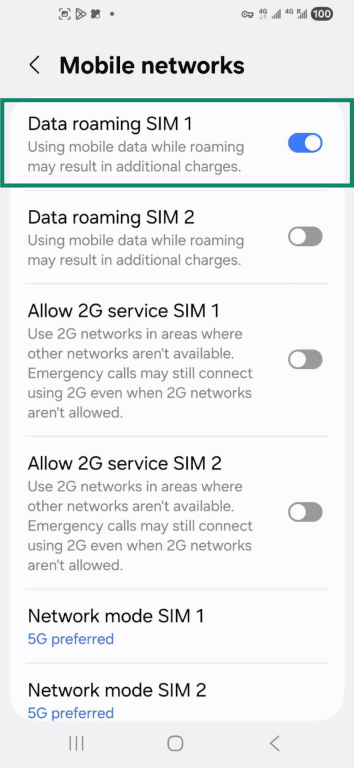
- Make sure mobile data on your preferred SIM is enabled. Then check if browsing works.
Check your internet connection on iOS
Here’s how you can check your internet connection on iOS devices.
First, check if your Wi-Fi is connected.
- Select Wi-Fi from your settings app.
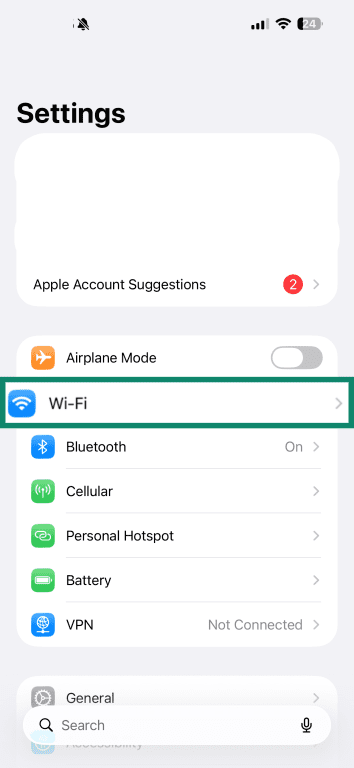
- Make sure the toggle is switched on. If you’re connected, you should see the name of the Wi-Fi network you’re connected to.
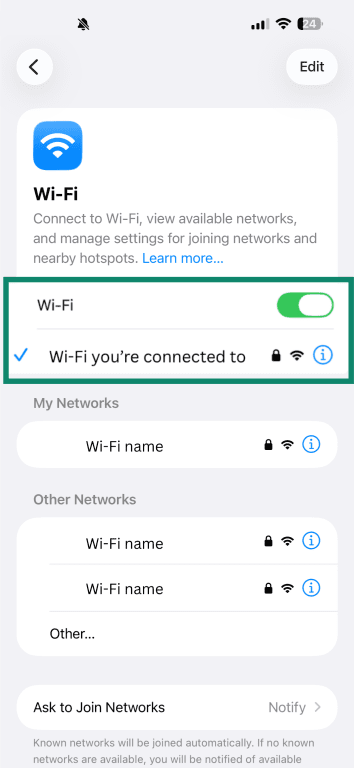
Follow these steps to see if your mobile data is working:
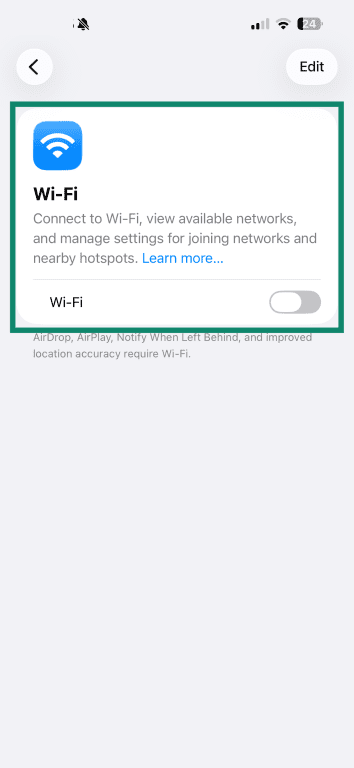
- Select Wi-Fi from your settings and turn it off.
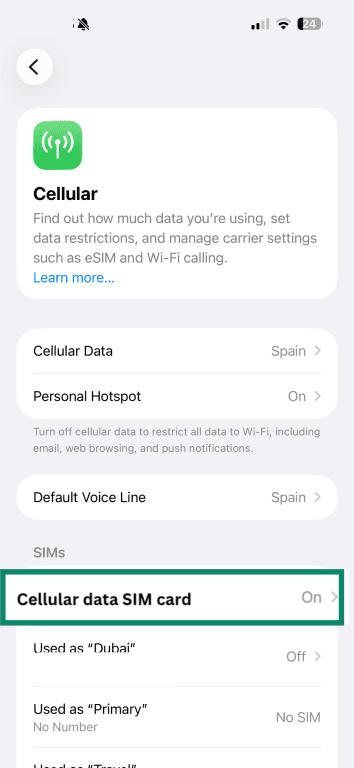
- Go back and select Cellular. Make sure the SIM you use for data is turned on. Then, open a browser and see if a webpage loads.
How to check your router and network connection
If your device settings look fine, but you still have no network connection, the issue may be with your router. While steps may vary by router model, the general idea is the same for most setups.
- Power: Check that your router is on and isn’t showing any warning lights.
- Cables: Make sure all cables are securely connected.
- Restart: Unplug your router, wait at least 30 seconds, then plug it back in.
- Local connection: Connect a device to the router using Wi-Fi or an Ethernet cable.
Here's how to check your router’s connection status through the router's administrator panel.
- Go to your Wi-Fi details in settings.
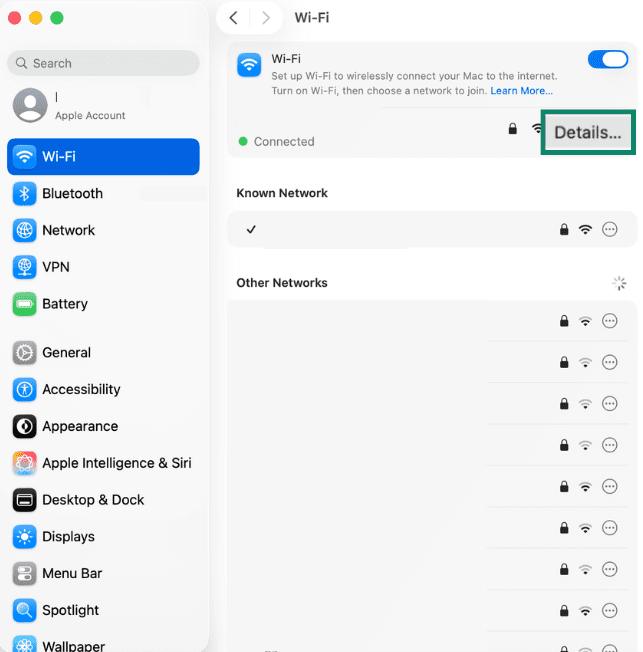
- Copy your router’s IP address (default gateway) from Wi-Fi details.
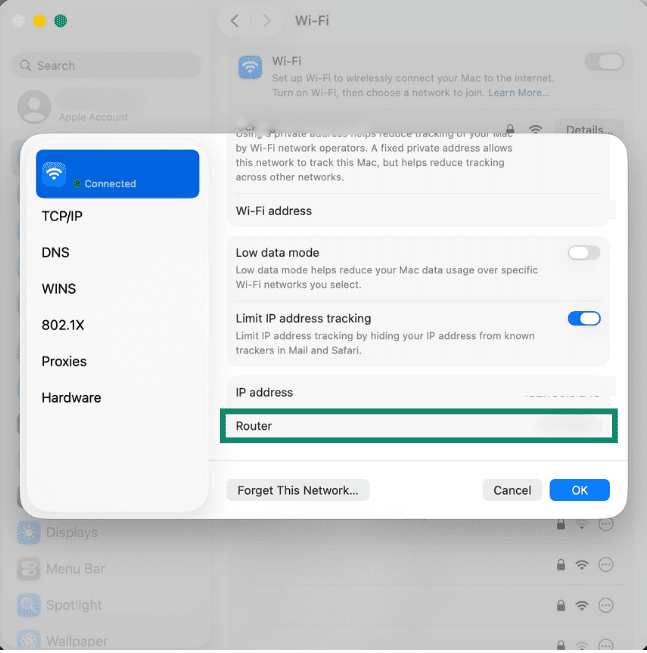
- Paste it into your browser. Your dashboard should show the connection status.
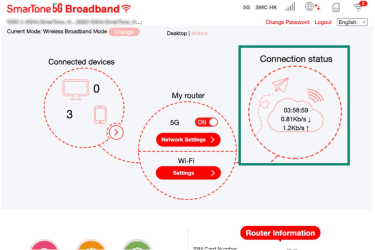
While these steps work in most cases, if your internet doesn't work even though it says you're connected, you may need additional troubleshooting help.
How to test your internet speed and performance
When you check your connection status on your router’s admin page, it might display your internet speeds, but this can vary by provider. If yours doesn’t provide this, here are other ways to check it.
Doing a ping test can also help diagnose other issues if your Wi-Fi connection looks okay, but you still can’t use the internet.
Using online speed test tools
Online speed test tools are the easiest way to check how your internet is performing. They measure key metrics such as download speed, upload speed, and latency. Two of the most trusted options include:
- Speedtest by Ookla: You can manually start a test and select a nearby server to obtain more detailed results.
- Fast.com: Runs automatically when the page loads and focuses primarily on download speed, making it a quick, simple option.
Since each service tests your connection slightly differently, running multiple tests helps confirm whether slow speeds are consistent or just a temporary fluctuation.
Checking ping, packet loss, and latency
Using the Terminal app (macOS) or Command Prompt (Windows) to check speed metrics can give you insight into how responsive and reliable your connection is, not just how fast it can download or upload data. Here you can see:
- Ping: Measures how long it takes for data to travel between your device and the server. Lower ping = faster response times, ideal for gaming, video calls, and browsing.
- Latency: Describes the overall delay in your connection, usually shown as an average ping value.
- Packet loss: Indicates whether data is being dropped during transmission. Even small amounts can cause buffering, choppy calls, and slow-loading pages, regardless of your internet speed.
Here's how to check these metrics on both Windows and Mac devices:
- Open the Terminal app (or Command Prompt for Windows).
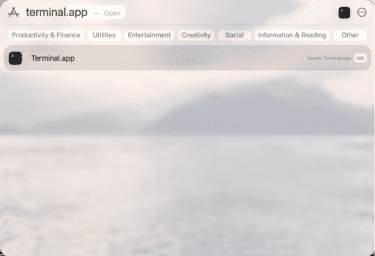
- If you’re using a Mac, type ping -c 20 1.1.1.1 and press Enter. If you’re using Windows, type ping -n 20 1.1.1.1 and press Enter.

- Wait until the test finishes, and check the output.
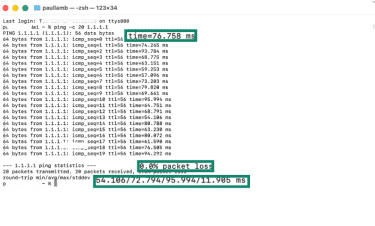
Here’s what the results mean:
- Ping results: Shown as response times in milliseconds (ms). Under 50ms is generally considered low and good for most activities, while over 150ms is considered high and may cause noticeable delays.
- Packet loss results: Shown as a percentage. Any packet loss can cause lag, buffering, or dropped connections, though levels below 1% are often acceptable for everyday internet activity.
- Latency result: Values represent average time in milliseconds (ms). This reflects the overall delay in the connection. Under 100ms usually feels responsive, while 100–200ms can feel sluggish, and anything above this may cause lag.
If the ping test didn’t work, but you appear to be connected to the internet, it could mean that your problem is coming from your DNS setup. You might need to take additional steps, such as clearing your DNS cache.
Learn more: How to lower ping and reduce lag while gaming
What affects internet speed and stability
Your internet speed and stability determine how smoothly you can browse, stream, or work online. A few key factors influence both; some you can control, others depend on your internet service provider (ISP).
1. Types of connections
The type of internet connection determines how fast and reliable your connection is. Here are the main options:
- Fiber-optic: Uses light instead of electrical signals, making it less prone to interference and typically the fastest and most reliable option. Upload and download speeds are usually comparable, making it ideal for streaming, gaming, and other heavy use.
- Cable internet: Offers good speeds and is widely available. The main drawback is shared bandwidth, which can slow speeds during busy hours.
- Digital subscriber line (DSL): Runs over phone lines and is easy to set up where lines exist. Speeds are lower than cable or fiber and drop the farther you are from your provider.
- Satellite or fixed wireless: Used where wired internet isn’t available. Speeds vary, but latency is usually higher. Weather, congestion, and signal quality can make these connections less reliable for gaming or video calls.
2. Network congestion
Congestion happens when too much traffic competes for limited bandwidth. This causes slowdowns, buffering, and jitter. At the ISP level, peak hours (evenings and weekends) overload shared infrastructure, reducing speeds for everyone on the network. This is especially true if multiple devices are streaming 4K video, downloading large files, or gaming.
To minimize it, schedule heavy use during off-peak hours or consider upgrading your plan for higher capacity.
3. Wi-Fi and router signal
Unlike with wired connections, Wi-Fi introduces variables that can cause speed and stability issues. This includes:
- The distance from the router and thick walls or floors can weaken the signal, reducing browsing speeds and increasing packet loss.
- Interference from neighboring networks, baby monitors, microwaves, or Bluetooth devices can introduce noise and degrade throughput, so router placement also matters.
- Older routers may not support modern network protocols or newer standards like Wi-Fi 6. This can cap performance even on fast broadband plans.
Switching to a wired Ethernet connection can help work around these issues while you diagnose and fix the underlying issue.
4. Hardware and devices
An outdated modem or router often can’t keep up with modern internet speeds, which means even a fast plan can feel slow.
Your personal devices also play a role. Older laptops, phones, and TVs often have weaker Wi-Fi support and may struggle to maintain stable, reliable connections.
5. ISP infrastructure and plan limits
Your internet performance also depends on your internet service provider’s infrastructure and the plan you subscribe to. Even if your home network is working properly, slowdowns can occur if local or regional networks are congested or undergoing maintenance.
Distance and routing paths also affect latency. The farther your data travels, the longer it takes to return, which can make activities like video calls or gaming feel less responsive. This does not necessarily mean your connection is broken, but it can explain occasional lag.
Finally, your plan sets the maximum speed available to your connection. Lower-tier plans have lower speed caps, and some plans reduce speeds after a certain data threshold is reached. Reviewing your plan details can help you determine whether your current speeds match what your tier allows.
Troubleshooting common internet connection problems
Identifying the root cause is key to fixing it. Here’s how to troubleshoot common connection problems.
Check your modem and router
- Restart your modem and router: Unplug both for about 60 seconds, plug the modem back in first, wait for it to fully reconnect, then power on the router.
- Check cables and connections: Make sure all Ethernet, coaxial, and power cables are securely connected and not damaged.
Confirm device connectivity
- Check your network connection status: Ensure Wi-Fi is turned on and your device is connected to the correct network.
- Airplane Mode: Confirm that Airplane Mode is disabled, as it turns off wireless connections.
- Test on a different device: Try connecting another phone, laptop, or tablet to see if the issue is device-specific.
Check your network settings
- Reconnect to the Wi-Fi network: Remove the network from your device, then reconnect and re-enter the password.
- Try a different frequency band: Switch between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz networks if both are available. This can resolve issues caused by congestion on one band or poor signal strength on the other.
Check for outages or maintenance
If none of your devices can connect to the internet, your ISP could be experiencing an outage or performing maintenance, which may interrupt service.
Check for interference
Wi-Fi problems are often caused by interference in your surroundings. Start by checking what’s near your router.
Ensure no electronic devices or physical barriers are causing connection issues. If in doubt, temporarily move these items away or turn them off and test your connection after each change.
Advanced troubleshooting (when basic fixes don’t work)
Checking network settings and firmware updates
Outdated or misconfigured router/modem settings can cause persistent slowdowns, instability, or limited performance even after restarts.
- Update your router’s firmware: Firmware updates can improve connection stability, patch security issues, and support newer devices.
- Adjust advanced router settings for better performance: Access your router's admin page and try changing channel width or disabling band steering (which auto-directs devices between bands) if it's causing connection drops. Manual channel selection can also avoid interference from neighbors.
When to contact your ISP
If you can’t resolve the issue, contact your ISP's customer support. It’s helpful to keep a log of everything you tried, as it might help them diagnose the problem more quickly.
You may be asked to provide your account details, the modem's MAC address (found on the device label or admin page), recent speed-test results, and a description of when the issues occur (e.g., across all devices, at specific times, or in certain apps).
FAQ: Common questions about internet connectivity
How can I check if my internet connection is working?
You can check your internet connection status via the network icon in your taskbar on Windows, the menu bar on macOS, or the settings on Android and iOS. You can also open a web browser and try loading a website. If you aren't connected, an error message will appear.
How do I test my Wi-Fi speed?
You can use online speed test tools to check your download speed. It may help to run multiple tests and compare results against your plan's advertised rates. It’s also possible to check ping, latency, and packet loss directly from your PC using Terminal on macOS or Command Prompt on Windows. Type ping -c 20 1.1.1.1 on macOS or ping -n 20 1.1.1.1 on Windows.
What should I do if my internet keeps disconnecting?
If your internet keeps disconnecting, try restarting your modem and router by unplugging them for about 60 seconds. Then, power on the modem, followed by the router. It’s also worth checking cables to ensure they’re securely plugged in and not damaged. If that doesn’t work, it’s worth trying more advanced troubleshooting steps.
Can background apps slow down my internet?
Yes, background apps on devices can use bandwidth and contribute to network congestion. This happens especially when multiple devices are running updates, streaming, or downloading at the same time. This can divide the available bandwidth and result in slower speeds per device. Limiting heavy background activity or scheduling it for off-peak times can often help.
What causes unstable internet connections?
Several factors can cause unstable connections, including Wi-Fi interference from distance, walls, microwaves, nearby networks, or household electronics. Network congestion can also affect stability, whether multiple devices are online at home or your ISP experiences heavy traffic during peak hours.
Take the first step to protect yourself online. Try ExpressVPN risk-free.
Get ExpressVPN