What is network jitter, and how does it impact internet performance?

Network jitter, or packet delay variation, happens when data packets experience inconsistent delivery times due to congestion or routing changes.
This inconsistency directly affects real-time applications like Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) and gaming, which require a steady data flow to function correctly and are highly sensitive to timing disruptions.
In this guide, we explain what causes network jitter, how it differs from other network issues, and what steps to take to fix it.
What is network jitter?
Network jitter is the inconsistency in how long data packets take to travel across a network. It can disrupt real-time applications like streaming, voice calls, and online gaming.
The technology behind jitter
All online traffic, from emails to video streams, is broken down into small units of data called packets. These packets travel independently from a source server to your device, where your device reassembles them in the correct order to present the final content.
Ideally, these packets arrive at a consistent and predictable rate. Network jitter happens when packets arrive too late, too early, or out of order. This lack of synchronization can make your internet feel slow by causing choppy video feeds, disrupted VoIP calls, and lag while gaming.
How jitter differs from latency and ping
Jitter can get confused with latency and ping, but it’s important to distinguish between them to accurately diagnose network performance issues.
Latency is the total time it takes for one data packet to complete a trip, and it can be measured as one-way or as a round-trip time (RTT). RTT is the measurement of that packet’s journey to the destination and back again. In other words, latency refers to the overall delay of a packet, not the variation in delay between packets.
Ping is used to measure latency. It sends a small test packet to a server and waits for a reply. The reported value is typically the RTT. Running multiple ping tests in sequence gives an idea of how responsive the network is over time.
Jitter measures the variation between those latency or ping results. If each packet takes roughly the same time to travel, jitter is low. But if packet delivery times fluctuate and are fast one moment and slow the next, then jitter is high. This inconsistency is what causes issues in real-time applications.
Types of network jitter
There are various kinds of network jitter. Understanding the differences between them can help identify the root cause of any network performance issues.
- Random jitter: Random jitter, as the name suggests, is jitter that displays unpredictable characteristics. The variations in packet arrival timings fluctuate constantly. Random jitter can stem from electrical or radio interference that causes noise in the network or irregular processing due to outdated or overloaded network hardware.
- Constant jitter: Constant jitter is a continuous and predictable level of packet delay variation in a network. The amount of variation remains relatively uniform over time.
- Transient jitter: Transient jitter is a brief but noticeable spike in delay variation caused by temporary disruptions like network congestion or wireless interference affecting individual packets. While short-lived, it’s enough to have noticeable impacts like video stutters, audio glitches, or lag spikes while gaming.
Causes of network jitter
Several factors can disrupt the orderly flow of data packets and cause network jitter.
Network congestion
One of the most frequent causes of jitter is network congestion, which occurs when too many devices attempt to use the network simultaneously and create a bottleneck. This slows down data packets and causes their arrival times to become inconsistent.
Interference on Wi-Fi
Devices like microwaves, baby monitors, or nearby Wi-Fi networks emit signals that can interfere with Wi-Fi, causing packets to be delayed or retransmitted.
Timing drift
Differences in device clocks and technical glitches can cause timing drift, which is when devices on a network aren’t synchronized with one another. Since networks rely on precise timing to send and receive data, this mismatch can cause packets to arrive at irregular intervals.
Hardware limitations
Outdated or underpowered network hardware is often a major source of jitter. Routers, switches, and even Ethernet cables that are old or low-quality may not have the processing power or capacity to manage modern internet traffic effectively.
Importance of quality network equipment
Using modern, high-performance network equipment is crucial for maintaining a stable connection. Quality routers and switches have faster processors and more memory, allowing them to handle heavy traffic loads without creating significant delays or jitter. Investing in good hardware provides a solid foundation for a reliable network.
Poor network configuration
Incorrect settings on network equipment can also create unnecessary delays and jitter. A poorly configured network may not be routing data efficiently, leading to network performance issues even if the hardware is capable of handling the traffic. Proper network configuration management is essential to ensure this doesn’t happen.
Impact of misconfigured routers
Misconfigured routers struggle to prioritize the necessary traffic or become overloaded during peak usage. Common router misconfigurations include poor Quality of Service (QoS) configurations or improper routing techniques. These problems can lead to packets being delivered inconsistently. The good news is that these configuration issues can be fine-tuned to improve jitter.
Bandwidth limitations or throttling
Jitter often happens when your connection doesn’t have enough bandwidth. This can occur when too many devices are online at once or when you’re streaming in high resolution or downloading large files. If your usage exceeds what your connection can handle, packets are forced to wait.
Another cause is internet service provider (ISP) throttling. This is when your ISP intentionally slows your connection. Throttling often starts during busy hours, or when you use your connection for certain activities like streaming or gaming. Since throttling places an artificial limit on your speed, it can cause packets to get delayed.
If your internet plan has low bandwidth, the only solution to this is upgrading your connection. However, if you’re experiencing throttling, ExpressVPN can help prevent content-based ISP throttling.
Effects of network jitter on performance
High network jitter impacts the performance of various online activities, especially those that depend on a real-time data exchange.
VoIP call quality issues
VoIP calls are extremely sensitive to jitter. For a conversation to sound natural, voice packets must arrive in a continuous and evenly spaced stream. When jitter is high, packets arrive out of order and cause the audio to sound distorted. It may even lead to delays in audio transmission or dropped calls.
Video conferencing challenges
Video conferencing requires a steady flow of both audio and video data. Jitter can cause video to freeze, pixelate, or lag behind the audio, resulting in a desynchronized feed.
Online gaming latency
High jitter can drastically hinder online gaming performance by making character animations look choppy and inconsistent on your screen. In shooter games, for example, you could be aiming at an opponent and would struggle to track their movement, as they’d appear to move erratically on your screen.
This isn’t necessarily as bad as input lag, which adds a noticeable delay to all your actions, but it’s still something that can significantly hinder performance in online games.
Business productivity impact
Beyond the productivity issues caused by the aforementioned video conferencing and VoIP call issues, jitter can directly impact systems that businesses rely on for productivity. For instance, financial trading systems require fast and consistent data delivery, but jitter can cause delays. This can potentially lead to missed trades and significant losses.
Measuring network jitter
Tools to measure jitter
There are several methods to check your internet speed and measure jitter on your network.
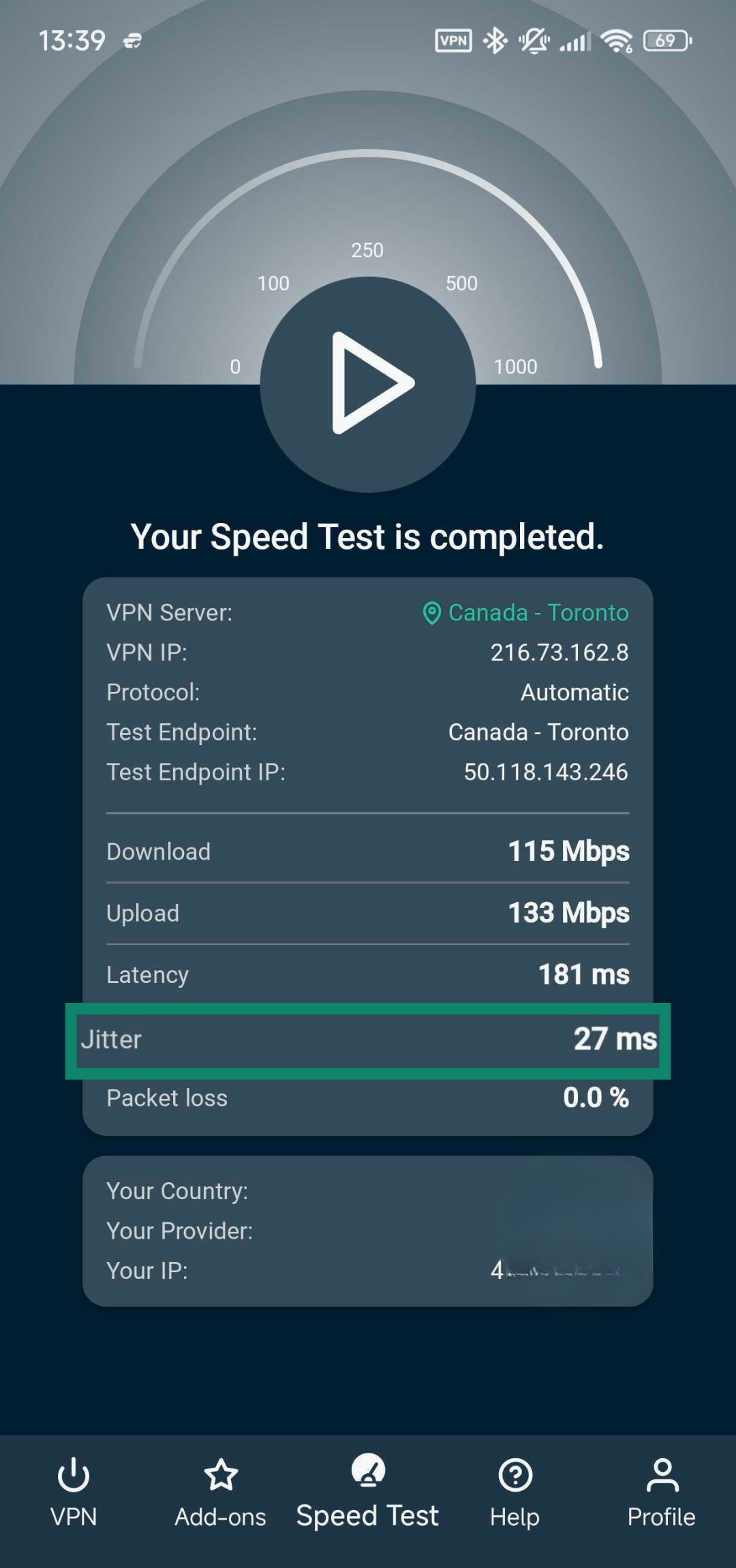
You can easily test jitter using the ExpressVPN mobile app, which includes a built-in speed test for connection speed, latency, and jitter. Here’s how to do it:
- Open the ExpressVPN app on your iOS or Android device and tap the Speed Test option at the bottom.
- Tap the play button to begin the speed test.
- Once the speed test is complete, look through the results to see what the jitter is on your network.
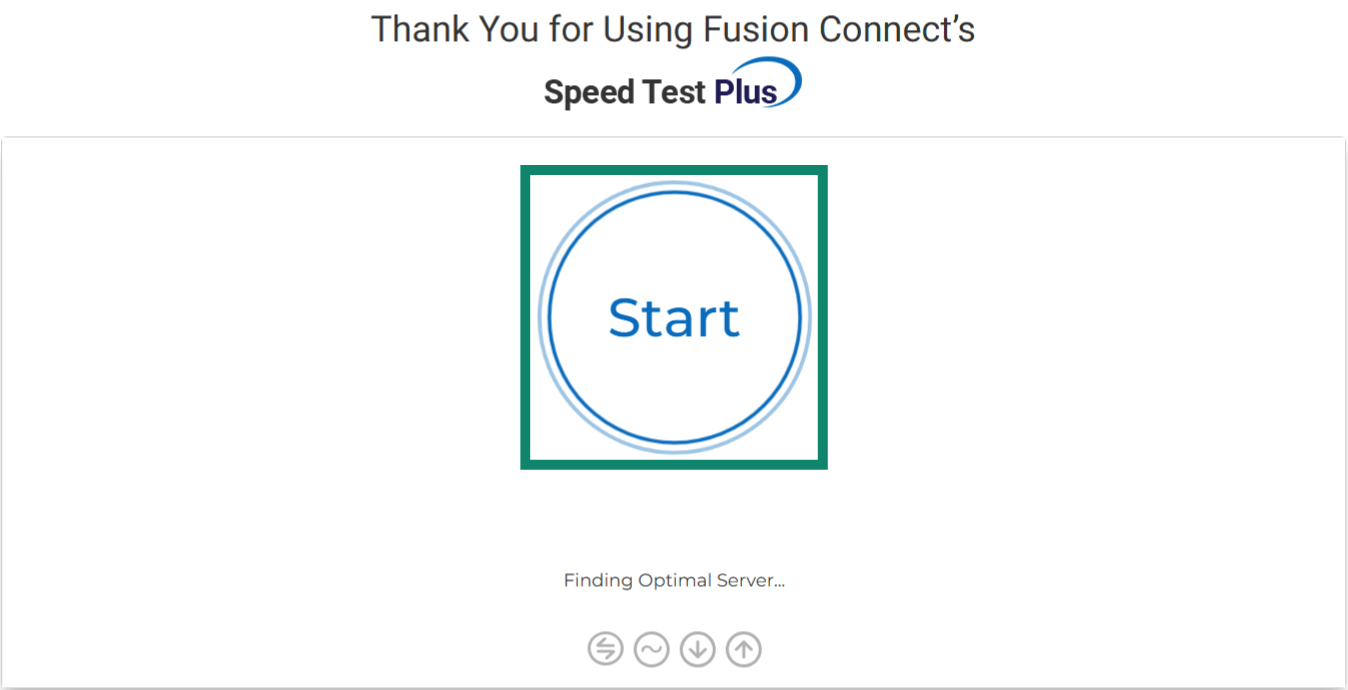
If you want to measure jitter on your desktop using a browser, websites like Fusion Connect have online tests that can pinpoint how much jitter your connection is experiencing. It’s a simple process:
- Access the Fusion Connect website and click the Start button.
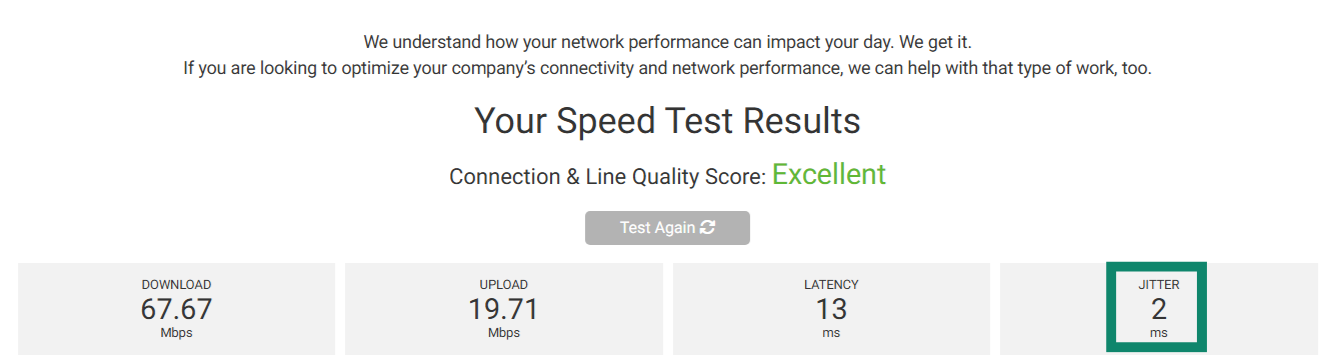
- Once the speed test finishes, you’ll see your connection’s jitter on the results page.
Another way to check jitter on your connection is through the ping utility. By consistently pinging a server and calculating the differences between the response times, you can determine how much the delay varies from one packet to the next, which is a reasonably accurate estimation of jitter. You can do this manually through your system’s command-line utility, but there are also online tools like Ping Test that can do it for you.
Successfully performing a jitter test
To get accurate results from a jitter test, prepare your network to ensure other network issues don’t affect the results. If possible, connect directly to your router with an Ethernet cable, as this will give you the most stable connection possible.
You should also close other applications that rely on the internet to make sure nothing is affecting your connection while you’re doing a jitter test.
How to interpret test results
Jitter values are displayed in milliseconds (ms). This number represents the average deviation from the mean packet delay. In simple terms, a lower jitter value is always better, as it indicates a more stable and consistent connection.
A single high reading could be a temporary issue. However, getting high jitter consistently on your tests points to a more persistent problem with your hardware, configuration, or ISP.
Acceptable levels of jitter
The acceptable levels of jitter generally depend on what you’re doing online.
What is a good jitter value?
As a general rule, a network jitter value of under 30ms is considered acceptable for most real-time applications like voice and video calls. Lower numbers are always better, with an ideal jitter measurement being as close to 0ms as possible.
If your jitter exceeds 30ms, you might start experiencing issues like choppy animations in online games, video-audio sync issues during video streams, pixelation during video conferences, and distortion in audio calls.
However, if you’re doing something that doesn’t rely too much on a consistent data stream, like streaming videos online or downloading files, jitter values up to 100ms shouldn’t have much of an impact.
Fixing network jitter
Solutions for home networks
For home users, fixing jitter often involves making the simple changes below to reduce local network congestion and improve connection stability.
Use Ethernet instead of Wi-Fi
A wired Ethernet connection is inherently more stable than Wi-Fi. Wireless signals are prone to interference from other devices and physical obstructions, which can cause packet loss and jitter. For activities like online gaming or important video calls, it’s a good idea to connect your device directly to the router with a cable.
Limit unnecessary bandwidth usage
Competition for bandwidth on your home network can cause jitter. If someone is streaming a 4K movie while you’re on a video call, both connections can suffer. Pause large downloads, updates, and other high-bandwidth activities during times when you need a stable, low-jitter connection.
Schedule updates and background tasks
Many applications and operating systems run automatic updates, which can cause a sudden surge of bandwidth use and lead to transient jitter. Schedule these non-urgent tasks to run during off-peak hours to avoid disrupting your real-time applications.
Business network solutions
Businesses can reduce jitter using more advanced network management techniques. These solutions provide greater control over how data traffic is handled, ensuring that critical applications always receive the priority they need.
Implement QoS to prioritize packets
Quality of Service (QoS) is a feature that can mark data packets to identify different services, and routers can then be configured to prioritize certain services over others. By configuring QoS, an IT team can instruct the network to handle VoIP and video conferencing packets before less time-sensitive data, for example.
Use a jitter buffer
A jitter buffer is a temporary storage area that collects incoming data packets and releases them at a steady, even pace. This mechanism intentionally delays the packets for a few milliseconds to reorder them correctly and smooth out the irregularities caused by packet delay variation.
Monitor and optimize your network
For businesses, proactive network management is essential. Using network monitoring tools allows administrators to track performance metrics like jitter, packet loss, and network latency in real time. This data helps them identify bottlenecks and optimize the network configuration to prevent jitter before it impacts users.
Choose the right VoIP provider
A high-quality VoIP provider can make a significant difference in call quality. Top providers build their networks to be resilient against jitter through features like jitter buffering. When selecting a provider, inquire about the specific technologies they use to ensure call clarity and reliability.
FAQ: Common questions about network jitter
What tools can I use to measure jitter?
You can measure jitter through various tools, like mobile apps and speed test websites. The easiest way on mobile is to use ExpressVPN’s iOS or Android app, which has a built-in speed test that measures jitter.
How do I fix jitter quickly?
The quickest fixes for jitter include switching to Ethernet from a Wi-Fi connection, closing unnecessary apps that are consuming bandwidth on your network, and scheduling automatic app and OS updates for a time when you’re not using your system.
What is jitter vs. latency?
Latency is the time it takes for a data packet to travel across a network. It can be measured as one-way travel or as a round-trip time (RTT). It represents the overall delay in the connection. Jitter is the amount of variation in that delay between packets. Latency tells you how long the trip takes, while jitter tells you how consistent the trips are.
Does jitter affect internet speed?
Jitter doesn’t affect internet speed, but it can still make a fast connection feel slow if you’re doing tasks like video conferencing, online gaming, or Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) calling.
Can jitter impact online gaming experience?
Yes, high jitter can cause you to experience choppy animations while gaming, which can be especially problematic in fast-paced and competitive online games where you need to react quickly to even the slightest movements.
How often should I test my network for jitter?
You should test your network for jitter whenever you notice symptoms like poor call quality, video freezing, or gaming lag. For general network health, running a test once a month can be beneficial. If you’re actively troubleshooting an issue, testing at different times of day can help you identify if the problem is related to peak usage hours.
Take the first step to protect yourself online. Try ExpressVPN risk-free.
Get ExpressVPN