Browser isolation: What it is and why it matters

From malicious ads to malware infections, there are many threats you might encounter while browsing the internet. The risks posed by hazards like malicious redirects and drive-by downloads can be mitigated by separating browsing activity from the rest of your device or network.
That’s essentially what browser isolation does. It’s an effective security feature for limiting the damage that web-based threats can cause. Browser isolation can take different forms, but it’s something both home users and business networks can benefit from. In this guide, we’ll explore how isolation can create a more secure browsing environment and the many dangers it guards against.
What is browser isolation?
Browser isolation refers to security features that create barriers between a web browser and the rest of the device it’s installed on. This means that if a web-based threat arises, the damage can be largely contained within the browser. Without any isolation, many threats could more easily affect entire devices and networks.
How does browser isolation work?
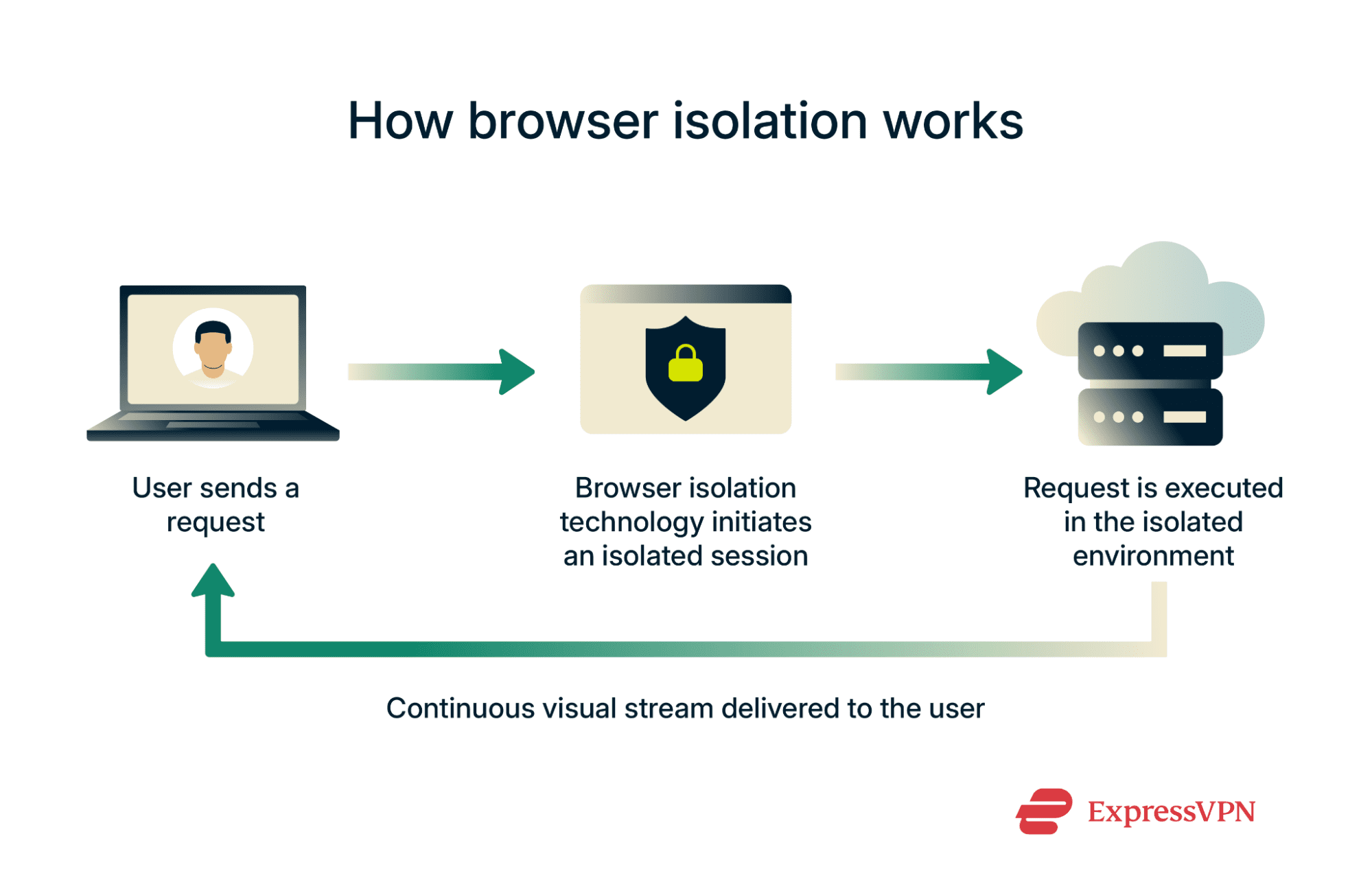 Typically, to browse the internet, you run a browser application on your device. Without isolation, any threats you might encounter could easily affect the rest of your device and, potentially, your wider network.
Typically, to browse the internet, you run a browser application on your device. Without isolation, any threats you might encounter could easily affect the rest of your device and, potentially, your wider network.
Browser isolation technology creates a degree of separation between your device and your browsing sessions. This could involve connecting to a cloud server or another device that actually does the browsing. Other methods involve running a browser in a sandbox or virtual machine.
Additionally, most modern browsers include less foolproof forms of isolation as fundamental features. This includes sandboxing individual tabs and the JavaScript engine, both of which limit the potential scope of dangerous scripts and malicious webpages.
It’s worth noting that similar techniques can be applied to other applications, not just browsers. Many developers use sandboxing to test apps in controlled, isolated environments, ensuring that they’re safe and reliable before running them locally.
Benefits of browser isolation
 Many organizations make use of browser isolation to safeguard their networks and reduce the impact that web-based threats might have on their devices or networks. Everyday users likewise gain added protection by using a browser that runs with basic isolation features. Here are just some of the many benefits it brings:
Many organizations make use of browser isolation to safeguard their networks and reduce the impact that web-based threats might have on their devices or networks. Everyday users likewise gain added protection by using a browser that runs with basic isolation features. Here are just some of the many benefits it brings:
Protection against web-based threats
The main benefit of browser isolation is added security. It’s an effective form of threat containment, guarding against everything from drive-by downloads and certain forms of phishing attacks to malicious ads and browser vulnerabilities.
Enhanced productivity and performance
In a business or organizational environment, browser isolation can also improve productivity by reducing the frequency and severity of security incidents. It minimizes the impact of zero-day exploits and protects sensitive data, so IT teams have fewer incidents to deal with and can focus their energies on other tasks. Some isolation systems also provide user analytics, helping enterprises track productivity.
Additionally, by stopping threats that might otherwise slow down devices, browser isolation can help organizations and individuals retain maximum device performance.
Improved compliance and data control
Businesses operating in certain industries, like healthcare and finance, need to comply with strict regulations with regard to the storage and access of data. Browser isolation can help by reducing the likelihood of problematic data leaks, breaches, and malware attacks that could put sensitive information at risk. It doesn’t offer complete protection against leaks, but it can reduce your attack surface.
What threats does browser isolation defend against?
 Browser isolation guards against a range of common browser-based threats. Isolation doesn’t necessarily offer full protection, but it can mitigate the danger posed by these common threats:
Browser isolation guards against a range of common browser-based threats. Isolation doesn’t necessarily offer full protection, but it can mitigate the danger posed by these common threats:
- Drive-by downloads: Simply loading a website can sometimes trigger unwanted or malicious downloads. Depending on the isolation method used, this threat could be virtually eliminated or significantly reduced.
- Malicious advertising: Certain ads contain malicious code or redirect users to unsafe sites. Even basic tab isolation will somewhat limit the ability of malicious ads to harvest user information.
- Redirect attacks: Cybercriminals can configure URLs to redirect users to different webpages than those they intended to visit. If your browser is isolated through virtualization, visiting a dangerous site is less likely to cause real harm.
- Browser vulnerabilities: Even the most popular browsers, like Google Chrome, can be coded in ways that create vulnerabilities. Cybercriminals can exploit these in unpredictable ways. By running a browser in isolation, the scope of such exploits is more limited.
Note, however, that browser isolation won’t protect against every possible web-based threat you might encounter. You may still inadvertently give away personal data as a result of phishing or be tricked into approving dangerous downloads.
Additionally, while isolation can mitigate the impact of web-based threats, like malicious websites and advertisements, it won’t stop you from encountering them. That’s why it’s important to remain vigilant, even when using browser isolation.
Types of browser isolation technologies
 There are three main forms of browser isolation.
There are three main forms of browser isolation.
Remote browser isolation (RBI)
As the name suggests, remote browser isolation (RBI) involves loading web pages and running browser activities remotely on an entirely separate device. All browsing activity takes place on cloud-based servers.
Rather than view and control an actual browser directly, the user instead sees a stream of what’s happening on the other device.
Alternatively, cloud-based servers can first remove all potentially dangerous code and elements from a page before displaying it to the user. Some remote isolation methods will even process each page and present it in a vector graphic format to the user.
Mostly used by businesses, RBI is arguably the most thorough form of isolation. It provides a high degree of protection from zero-day exploits and web-based threats.
On-premise solutions
On-premises isolation (also referred to as on-premise or on-prem) works a lot like RBI, except the server that hosts and handles the web content is set up and managed by the users themselves and is situated on their premises. A business, for example, might set up its own internal servers to host browsing activity, negating the need for a cloud vendor.
Deploying isolation on-premise provides more control and customization to the organization, as admins are fully responsible for managing and maintaining their servers and associated infrastructure. At the same time, on-premises isolation lacks the scalability of RBI, and the costs of owning and operating your own servers can quickly add up.
Client-side isolation
With client-side isolation, the isolation is performed within the user’s device rather than on a separate server or in the cloud. Special software creates a separate, walled-off environment that handles browsing activity. This is usually done in one of two distinct ways:
- Virtualization: This essentially divides a device into multiple separate virtual machines, each of which can run its own OS, browsers, and other apps.
- Sandboxing: This creates a contained virtual environment that is still run within a device’s primary OS.
Everyday users are most likely to benefit from client-side isolation. Most major browsers execute a degree of sandboxing between tabs. For added protection, home users with more technical knowledge can take advantage of free virtualization tools. For example, you may want to open your browser within a sandboxed version of your OS to provide an extra layer of isolation.
Client-side methods of browser isolation generally aren’t as comprehensive as remote options, but they still make browsing the internet safer.
Browser isolation vs. traditional web security
 Fundamentally, browser isolation and traditional web security tools work in different ways. Both provide protection, but the underlying technology differs significantly.
Fundamentally, browser isolation and traditional web security tools work in different ways. Both provide protection, but the underlying technology differs significantly.
Key differences and complementary roles
Some of the major differences between browser isolation and other cybersecurity measures include:
- Availability: Aside from the sandboxing built into most browsers, browser isolation is most commonly used by organizations and tech-savvy individuals. Individual users can set up isolation systems, but the cost and resources involved tend to make this more of an enterprise-level solution.
- Functionality: Browser isolation separates browsing activity from a user’s device by running the browser in sandboxes, virtual environments, or on another device or server. Traditional security tools, meanwhile, tend to run on the user’s device or network, blocking threats as they appear.
- Approach: Generally speaking, traditional web security uses a reactive approach, relying on databases and behavioral analysis to detect and block threats. Isolation, meanwhile, is more proactive, treating all web content as potentially malicious.
- Vulnerability: Traditional web security relies on vast lists of known malware, dangerous sites, and exploits to block threats. Though they also generally use behavioral analysis, antiviruses can still be vulnerable to zero-day attacks. Isolation, especially the most extreme forms, can mitigate or even eliminate the damage caused by zero-day threats by keeping them away from vital systems.
Despite these differences, traditional web security tools and browser isolation technology work well together. For the highest level of digital security, it’s a good idea to combine RBI with antivirus software, secure web gateways, and other tools.
Practical use cases for browser isolation
 Browser isolation can be deployed in various situations where additional web security is needed. The most robust forms of isolation are commonly used in contexts where cyberattacks are likely or especially sensitive data is handled.
Browser isolation can be deployed in various situations where additional web security is needed. The most robust forms of isolation are commonly used in contexts where cyberattacks are likely or especially sensitive data is handled.
Enterprise remote work security
More and more businesses now operate with remote or hybrid teams of workers, who may need to access sensitive company files or web apps on personal networks. Such environments often lack the sophisticated security of office networks. Browser isolation can be an effective way to reduce the risks that come with remote workers using the internet.
Financial industry threat mitigation
Cybersecurity is particularly important in the finance world, where banks and payment providers are often targeted by cybercriminals. RBI can help protect financial institutions from a myriad of web-based attacks, safeguarding sensitive data and securing digital transactions.
Government and military use of isolation
Many governmental agencies are increasingly turning to browser isolation to help protect sensitive data and state secrets. Isolation technology provides extra protection against targeted attacks that might result in devastating data breaches or sabotage.
Cybersecurity in education environments
Educational institutions also handle large amounts of sensitive data and must abide by strict compliance regulations. Browser isolation can help them remain compliant, keeping student and faculty data safe and networks protected from various threats.
Everyday use
While the average internet user is unlikely to make use of full browser isolation, they can benefit from certain, more limited features included in popular browsers, like Google Chrome and Mozilla Firefox.
These features usually rely on site isolation, which shares principles with browser isolation but has a more limited scope. With site isolation, each tab is run as a separate process, reducing the risk that a malicious site can steal your information. A degree of sandboxing also mitigates the damage that web-based threats can cause to the rest of your OS.
Technical users or those worried about being targeted for various reasons can also deploy client-side isolation. By installing free virtualization tools and running your browser within a sandbox, you can browse with added safety measures in place.
How to choose the right browser isolation solution
Though primarily designed for organizational use, individuals may still be interested in integrating browser isolation into their internet setups.
Home users not satisfied with the limited level of isolation afforded by modern browsers may want to look into free sandboxing tools. Though quite distinct technologically from browser isolation tools, using a virtual private network (VPN) is another way to enhance online security. Rather than offering compartmentalization from the rest of a device, a VPN can effectively separate a user’s browsing activity from their network by encrypting the connection and routing it through a remote server. Related solutions include using a privacy-focused browser and adopting best practices like browser compartmentalization.
Enterprises, meanwhile, should consider the options with care. Not all browser isolation methods and solutions are equal, as they can vary greatly in fields like pricing, usability, and security.
Evaluation criteria
- Type of browser isolation: First, administrators should decide whether they want to opt for RBI or an alternative method, like client-based or on-premise isolation. RBI is often the safest option, but other methods may be preferable depending on the specific use case.
- Level of isolation: Full browser isolation involves a complete separation between the end-user’s device and the browser, with content rendered as a series of images or a video stream. Partial isolation, which sees at least some of the web code executed on the user’s device, is less secure but may be sufficient in some circumstances.
- Usability and integration: Browser isolation technology can be relatively complicated, particularly for new users who are unfamiliar with how it all works. Smaller and less experienced businesses may prefer simpler solutions.
- Pricing: Commercial isolation providers often charge fees, with prices varying depending on the technology used, the number of users, and other factors. It’s important to take your budget into account when considering the options.
- Scalability: As your business grows and changes, you may find that you rely more heavily on browser isolation or need to add new users as your workforce expands. If so, it helps to have a scalable solution. This generally means looking for a cloud-based provider.
- Vendor reputation: It’s also worth taking a look at the reputation of any cloud vendor or isolation provider you’re thinking about working with. Some providers naturally have stronger track records than others in areas like support, security, and privacy.
Integration and deployment options
There are numerous ways to deploy browser isolation technology, including setting up your own on-premise servers or paying cloud vendors to take on most of the work. Some tools integrate more easily with other security solutions, like secure web gateways. Admins should consider their existing security stack and think about short- and long-term needs when deciding on the most appropriate solution.
FAQ: Common questions about browser isolation
Is browser isolation the same as a secure browser?
No, browser isolation and secure browsers are different, though both share a common goal of improving online security. Browser isolation involves separating or isolating browsing activity from a user’s device in order to prevent or mitigate threats. Secure browsers, meanwhile, are browsers with various security features built in, like data encryption, advanced privacy settings, and, in some cases, VPNs.
Can it completely block malware?
Browser isolation can reduce the risk of browser-delivered malware infiltrating your device or network. That said, it is not a flawless solution for malware protection. For the best possible defenses against malware, pair browser isolation with other tools.
Does browser isolation slow down performance?
It really depends. Some methods of browser isolation will cause noticeable increases in latency. This is especially true when traffic must be redirected via a cloud-based system. Other methods for isolating a browser will not result in any discernible impact.
Is RBI better than client-side isolation?
From a security standpoint, remote browser isolation (RBI) is more robust since it executes all browsing activity in a remote, isolated environment, completely cut off from the user’s device and network. A downside of this is the introduction of latency. Depending on the specific method used, client-side protection can still offer a high degree of isolation even without making use of a second device. Neither method is definitively better, but organizations and high-security environments tend to use RBI.
Is browser isolation effective and safe?
Generally speaking, yes, browser isolation is a safe and effective method of improving security while browsing. Remote isolation, in particular, offers substantial security benefits, making the delivery of various kinds of web-based threats significantly harder.
How do I disable or remove browser isolation?
The process to disable or remove isolation varies depending on the type of isolation technology you’re using. Often, you’ll need to access the isolation administration console and make the necessary changes from there.
Take the first step to protect yourself online. Try ExpressVPN risk-free.
Get ExpressVPN