Is Amazon safe? A complete guide for smart shopping

Amazon is one of the world’s largest online marketplaces, used daily for everything from household essentials to high-value electronics. But “safe” can mean different things depending on what you’re buying, who you’re buying from, and how you manage payments, shipping, and account security.
This guide breaks down the most common risks shoppers run into on Amazon and explains how Amazon’s protections work in practice. It also outlines practical steps to shop more confidently, spot red flags early, and reduce the chance of losing money or personal data.
Is Amazon safe to buy from?
Amazon is generally safe to buy from, especially when you take basic precautions. Issues shoppers most commonly run into concern things like misleading listings, inconsistent product quality, counterfeit items in high-risk categories, and occasional delivery or return disputes.
How Amazon handles buyer security
Amazon uses several account- and platform-level controls intended to reduce unauthorized access and provide a clear path to verify or report suspicious activity.
Its main protections include:
- Two-step verification: Amazon allows buyers to secure their accounts using two-factor authentication (2FA), which adds an extra step when signing in, such as a one-time code sent by text or an authenticator app. This helps prevent unauthorized access if a password is compromised. Amazon also uses automated systems to detect unusual sign-in attempts and may require additional verification when a login appears risky, such as from a new device or location.
- Security alerts: Amazon issues security alerts for certain account events and access activity. In some cases, users may be asked to confirm whether a sign-in or action was authorized before proceeding.
- Customer support and scam reporting: Amazon provides a dedicated reporting channel for suspicious emails, texts, calls, or websites that claim to be from Amazon and states it does not initiate contact to request sensitive credentials such as passwords or verification codes.
Encryption and payment safety
According to its Privacy Notice, Amazon protects personal information during transmission using encryption protocols and software and handles credit card data in line with the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), a set of security requirements designed to reduce the risk of card data exposure during payment processing and storage.
For orders placed with third-party sellers through the standard checkout flow, Amazon processes the payment and sends funds to the seller without sharing the buyer’s payment information with that seller.
Amazon A-to-Z Guarantee
Amazon’s A-to-Z Guarantee is designed to protect customers who purchase physical items from third-party sellers on Amazon. It allows buyers to request a refund if an order does not arrive, arrives damaged, or is materially different from the seller’s description, and the issue cannot be resolved directly with the seller.
If a buyer contacts the seller and does not receive a satisfactory response, Amazon may step in to review the case and decide whether a refund is appropriate under the guarantee.
The A-to-Z Guarantee applies to eligible purchases made through Amazon’s marketplace. Coverage, eligibility requirements, and resolution processes vary by region, and Amazon publishes region-specific versions of the policy (for example, for the U.S., U.K., and EU).
Not all purchases are covered. Amazon states that the A-to-Z Guarantee does not apply to certain categories, including digital products, services, stored-value items such as gift cards, and other exclusions listed in the policy.
To be considered, buyers must submit an A-to-Z Guarantee claim within the timeframe specified by Amazon and follow Amazon’s instructions for contacting the seller and, when required, returning the item.
Risks of buying on Amazon
Here are the most common tactics and red flags of an Amazon scam:
- Impersonation messages: Scammers sometimes pose as Amazon or delivery partners using look-alike emails, fake order confirmations, or fraudulent tracking links. These messages are designed to steal logins or payment details.
- Fake sellers and counterfeit products: Some sellers use Amazon’s Marketplace to disguise low-quality or counterfeit products as legitimate listings. These can be difficult to detect until after delivery, especially in high-demand categories like electronics, cosmetics, or collectibles.
- Off-platform payment requests: All legitimate orders go through Amazon’s own checkout system. Requests to send money directly to a seller fall outside that process and are a clear indicator of a scam.
- Manipulated reviews: Some listings inflate their reputation through fake or paid reviews. Warning signs include repetitive short reviews, vague language, or mismatched star ratings.
- Diversion to fake support channels: Some scammers try to move the conversation away from Amazon’s normal channels by supplying a phone number, chat link, or website that looks like customer support but is not operated by Amazon. These interactions are designed to control what information is presented and to capture sensitive details (for example, account credentials or one-time codes).
Safety tips for Amazon shoppers
Many risks on Amazon can be avoided by following a few straightforward guidelines for secure online shopping.
Verify seller credibility
While these simple checks can never fully rule out a scam, you can filter out the majority of suspicious vendors before ever making a purchase.
- Review seller ratings: A high percentage of positive feedback over a long period can suggest consistent performance, while repeated negative comments or little to no seller history can indicate an inexperienced seller or one that may warrant closer scrutiny.
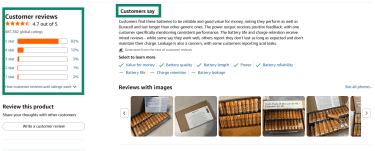
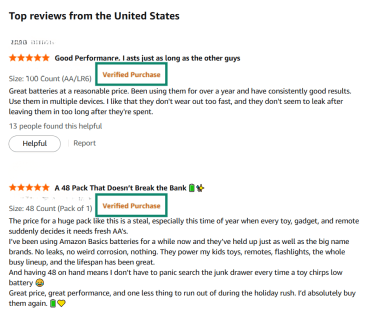
- Look for Verified Purchase reviews: While this doesn’t guarantee a review is unbiased or accurate, it does confirm the reviewer purchased the product via Amazon.
- Investigate brand and listing consistency: Counterfeit risk is often reflected in inconsistencies within the listing itself. Examples include unusual or slightly altered brand names, product photos that do not match each other, or branding on the item that differs from what is shown in the listing. These kinds of mismatches can indicate a higher chance that the item received will not match the advertised product.
Keep your payments secure
- Keep payments within Amazon checkout: Amazon processes payments for Marketplace orders and does not share your payment information with third-party sellers. Requests to send money directly to a seller fall outside Amazon’s normal order flow.
- Understand gift card scam patterns: Amazon gift cards are a valid payment method, but scammers often misuse them. A real Amazon purchase will only ask you to enter a gift card claim code during checkout on Amazon’s website or app. Amazon will never ask for gift card numbers, claim codes, or PINs by email, text message, phone call, or chat. Any message that pressures you to share a gift card code outside the checkout process is a strong sign of a scam.
- Watch out for spoofed payment pages: Ensure the URL begins with “https://” and says “amazon.com” before entering payment information. Avoid clicking links in unsolicited emails or messages that may be offering deals or coupons, as these could be phishing scams designed to steal your data.
Avoid too-good-to-be-true deals
A steep discount that is far below comparable listings can be a warning sign, particularly when it appears alongside unclear product information or a seller with limited history. In these cases, the main risk is that the item received may be materially different from the listing, including counterfeit or low-quality goods.
Should you use a VPN when shopping on Amazon?
Using a virtual private network (VPN) can be helpful when you’re shopping on Amazon over public or shared Wi-Fi, such as in cafés, airports, hotels, or coworking spaces. On these networks, a VPN encrypts your internet connection, which can reduce the risk of other people on the same network monitoring or interfering with your traffic while you browse or check out.
A VPN also replaces your device’s IP address with the VPN server’s IP address. This can limit how much information a public network operator or local observers can infer about your connection, such as your approximate location.
However, a VPN doesn’t hide information you choose to share with Amazon, including your shipping address, payment details, or account activity. It also doesn’t change what Amazon can see and record when you’re signed in to your account. A VPN’s role is to protect the connection itself, not to make you anonymous to the service you’re using.
Amazon vs. third-party sellers
Amazon sells some products directly and also hosts independent third-party sellers on its store. Independent sellers represent a major share of activity in Amazon’s store, as they account for more than 60% of sales.
You can usually tell who you’re buying from by checking the product listing details. Amazon listings clearly show “Sold by” and “Ships from” information, which indicates whether Amazon itself or a third-party seller is responsible for the sale and fulfillment.
- Sold by Amazon, Ships from Amazon: Amazon is both the retailer and the fulfiller. These purchases are covered by Amazon’s standard customer service, return, and refund policies.
- Sold by a third-party seller, Ships from Amazon (Fulfilled by Amazon): The seller owns the product, but Amazon handles storage, shipping, and customer service. Payment is still processed through Amazon.
- Sold by a third-party seller, Ships from the seller: The independent seller manages fulfillment and often handles customer service directly, though payment still goes through Amazon.
This distinction matters for safety and dispute resolution. When issues arise (such as items not arriving, arriving damaged, or not matching the description), Amazon can step in through its A-to-Z Guarantee for most third-party purchases. However, response times, return processes, and communication quality can vary more with independent sellers than with Amazon-sold items.
Amazon refund process and scam reporting
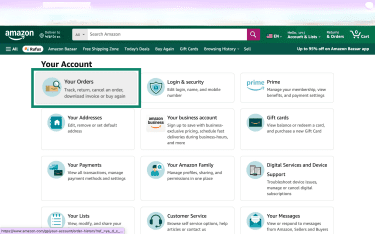
The exact steps and available options may vary depending on the item, seller, and region, but the refund process generally begins in Your Orders.
How to request a refund if the item was sold and shipped by Amazon
- Sign in and open Your Orders.
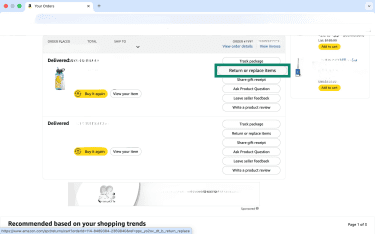
- Next to the relevant item, select Return or replace items.
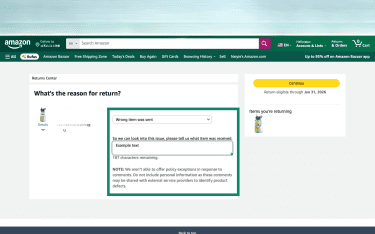
- Choose the return reason and follow the on-screen steps to submit the request.
How to request a refund if the item was sold by a third-party seller
When an order shows “Ships from (Seller Name),” the seller generally handles customer service first. If the issue is not resolved and the order qualifies, the A-to-Z Guarantee process is the escalation path Amazon describes for certain delivery and item-condition issues.
- Log into your Amazon account and go to Your Orders.
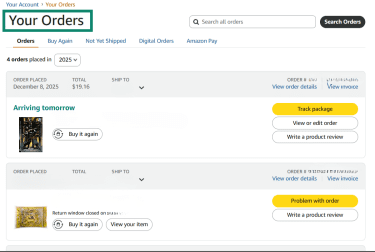
- Locate your order and then choose Problem with order.
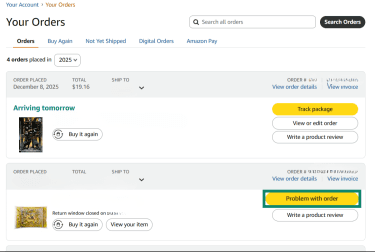
- Choose a reason for the return and add comments explaining the problem.
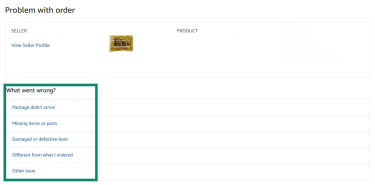
- Submit the request by clicking the Send button.
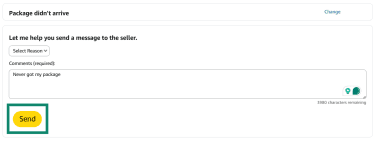
From here, Amazon will review the refund request. To view the status of your request, relocate your order, and choose Problem with order.
After Amazon has reviewed the refund request, they may either grant a full refund without additional steps required, or you may need to mail the item back to the fulfillment center following any instructions they provide.
Steps to report fraud or issues
- Log relevant details to the case, such as screenshots, communications with the fraudulent seller, and order details.
- Log into your Amazon account and open the customer service page.
- Choose Report suspicious activity.
- From the list provided, choose the most relevant option for your case.
- Choose if you want to chat with or call an agent. From there, provide the details you collected earlier.
Customers can also report suspicious communications through Amazon’s scam reporting page.
FAQ: Common questions about Amazon safety
Is Amazon safe to use with my credit card?
Amazon protects payment information in transit using encryption protocols, and it handles credit card data in line with standard industry requirements. For third-party Marketplace orders placed through Amazon’s checkout, Amazon processes the payment, and the seller does not receive the buyer’s payment information.
What should I do if I receive a fake item on Amazon?
Contact the seller through Amazon, request a refund, and stop using the product. You can also report the issue to Amazon.
Can I trust Amazon reviews?
Amazon reviews can be a helpful reference point, but they’re best treated as one signal rather than a guarantee of product quality or authenticity. Some reviews are labeled Verified Purchase, which means Amazon has confirmed that the reviewer bought the item through Amazon at a price it considers typical. Reviews without this label can still appear on product pages.
Amazon has rules that prohibit review manipulation and states that it takes action against fake or misleading reviews. That said, no review system is perfect, and biased or inaccurate reviews may still slip through. For a clearer picture, it helps to look at patterns across many reviews, check recent feedback, and pay attention to detailed comments rather than relying on ratings alone.
How do I know if an Amazon seller is legit?
Check the seller’s ratings and reviews, then examine the product listing for consistency and signs of counterfeiting. While no method is foolproof, sellers with a longer history and realistic, detailed reviews are generally lower risk than new or unreviewed sellers.
What protections does Amazon offer for third-party purchases?
Amazon’s A‑to‑Z Guarantee covers a wide range of products sold by third-party merchants. The guarantee allows you to contact Amazon directly for a refund if an item is defective or not as described.
Take the first step to protect yourself online. Try ExpressVPN risk-free.
Get ExpressVPN