Expressvpn Glossary
Endpoint security
What is endpoint security?
Endpoint security (or endpoint protection) is a cybersecurity approach that safeguards individual devices, such as computers, mobile phones, servers, and Internet of Things (IoT) devices, from malicious activity.
Because these devices connect to networks and cloud services, they can serve as potential entry points for attackers. Endpoint security solutions apply protective measures directly on each device to detect, block, and respond to threats.
How does endpoint security work?
Endpoint security operates by monitoring and protecting devices that connect to a network. A lightweight security agent is installed on each device to track activity and enforce protection measures such as firewalls, antivirus scans, and data encryption.
These solutions use multiple layers of defense to detect and block threats, including malware, ransomware, and phishing, before they can move across the network.
In larger environments, endpoint security systems are often managed through a centralized, cloud-based platform that enables administrators to deploy updates, monitor devices, and respond to incidents in real time.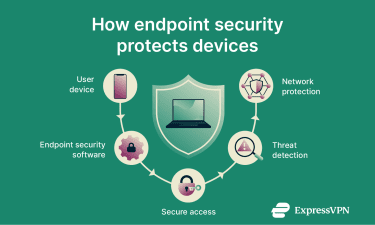
Why is endpoint security important?
Endpoint security is a key component of protecting data and systems from cyber threats that target individual devices. It reduces the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access by ensuring that every device connected to a network follows consistent security standards.
In distributed or remote work environments, endpoint security helps safeguard network connections and maintain compliance with data protection requirements. By securing each endpoint, organizations strengthen their overall defense against malware, ransomware, and other network-based attacks.
Types of endpoint security solutions
Endpoint security brings together multiple tools to protect devices. The most common types include:
- Antivirus and anti-malware software: Detect, block, and remove malicious programs such as viruses, trojans, and spyware from individual devices.
- Firewalls and intrusion prevention systems (IPS): Monitor network traffic to block unauthorized access and stop attacks before they reach the device.
- Data loss prevention (DLP) tools: Prevent sensitive information from being shared, copied, or transmitted outside approved channels.
- Endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions: Monitor devices for suspicious behavior and provide alerts or automated responses to contain potential threats.
- Virtual private networks (VPNs) and encryption technologies: Protect data in transit by creating secure, encrypted connections that prevent interception or tampering.
Endpoint security vs. network security
Unlike endpoint security, which protects individual devices, network security focuses on the routes and pathways that enable communication and data exchange between them.
Network security takes a perimeter-based approach, defending the underlying infrastructure from external and internal threats. It relies on technologies such as firewalls, VPNs, and intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS) to monitor, filter, and block malicious traffic.
While endpoint security contains compromised devices to stop threats from spreading, network security prevents those threats from entering or moving through the network in the first place. It prevents network-wide threats such as distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, lateral movement, and data breaches.
Common endpoint security threats
Endpoints face various threats that target both devices and the people using them. Some of the most common examples include:
- Phishing and social engineering attacks: Use deception to trick users into revealing sensitive information or installing malicious software through emails, messages, or fake websites.
- Malware and ransomware infections: Infect systems to damage files, steal data, or lock information until a ransom is paid.
- Unauthorized device access: Exploits weak passwords or misconfigured settings to gain control of devices and expose stored data.
- Data exfiltration or credential theft: Takes confidential information or steals login details to gain access to networks or cloud services.
- DDoS attacks: Overwhelm network resources with excessive traffic, disrupting connectivity and access to services.
Further reading
- What is cybersecurity, and why is it important?
- VPN vs. antivirus: Key differences and which one you need
- Online shopping safety tips
FAQ
What does endpoint security protect?
Endpoint security protects individual devices such as computers and mobile phones from cyber threats that target data, applications, and system processes. It protects both stored information and activity that takes place on the device.
How does endpoint security detect threats?
Endpoint security detects threats by monitoring device activity for known attack patterns or suspicious behavior. It uses tools such as antivirus scanning, behavioral analysis, and threat intelligence to identify and respond to malicious activity.
What’s the difference between endpoint and antivirus protection?
Antivirus protection detects and removes malware from a device. Endpoint security is broader, combining antivirus tools with features like firewalls, data encryption, and centralized management to protect multiple devices across a network.
Do I need endpoint security at home?
Endpoint security isn’t limited to large organizations. Home users also benefit from securing personal devices that connect to the internet or shared networks. VPNs, antivirus software, and firewalls provide basic endpoint security for most households.
More advanced tools, such as endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions, are typically used in business environments where multiple devices require centralized management and monitoring.
