Does Alexa spy on you? Simple ways to protect your privacy

Amazon Alexa devices, like the Echo Dot and Echo Studio, do not spy on users or listen in on private conversations, but they can sometimes activate inadvertently without the user knowing.
Alexa devices have to listen for and record voice commands to function, and may mistake background chatter or even sounds from a TV, computer, or podcast as an instruction.
Fortunately, there are ways to better protect your privacy and reduce these occurrences while still enjoying your Alexa devices.
How Alexa works and why it matters for privacy
Before we start talking about privacy concerns, it’s important to understand how Alexa works. So, let’s begin with a look at the system’s core functions, including its “always on” listening abilities and “wake word” functionality.
Key functions and voice recognition
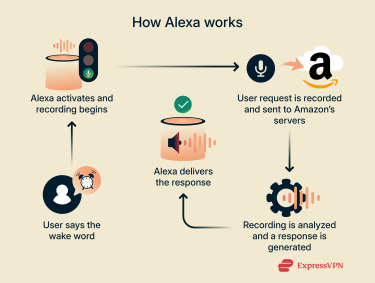 Alexa devices, as well as other smart speakers, are voice-activated. They’re powered by voice recognition technology, which allows them to understand and respond to the user’s audio commands. A typical interaction works as follows:
Alexa devices, as well as other smart speakers, are voice-activated. They’re powered by voice recognition technology, which allows them to understand and respond to the user’s audio commands. A typical interaction works as follows:
- The user says the Alexa “wake word,” which activates the device.
- Upon hearing the wake word, Alexa activates and begins recording audio.
- The user issues their command or query, which is sent to Amazon’s cloud servers for processing.
- The voice recording is processed, and a response is generated.
- Alexa responds to the user in its own voice.
How the wake word “Alexa” activates listening
Alexa devices are designed to activate only when a specific wake word is spoken. Common wake words include “Alexa,” “Echo,” and “Amazon,” and it’s only when you say your specific wake word that the device will activate, listen in, and record whatever you say next.
Thanks to this, Alexa shouldn’t be able to listen or record without your knowledge or consent. However, Alexa is always processing surrounding sounds to listen for its wake word, and it can sometimes make mistakes, with so-called ‘false triggers’ being misinterpreted as wake words and activating the device’s recording features.
What happens after a false trigger
If an Alexa device mistakenly interprets some background noise or conversation as a wake word, it will activate. The device’s light will turn blue, indicating that it is actively listening, and it will record a brief snippet of audio to send to the cloud for processing.
In most cases, the cloud algorithms will detect no clear command or question, and the device will go back into passive mode. However, if any of the background noise happens to resemble a command or query, Alexa may attempt to respond to it.
Does Amazon store or share your voice data?
Yes, by default, Amazon stores all voice recordings on its servers. It does not share raw voice data (the actual recordings), but it can share the content of the interaction with third parties, including skills developers and advertisers. In addition, Amazon may allow a small number of human reviewers to listen to and analyze some voice recordings to help improve Alexa’s speech recognition and understanding, but you can opt out of having your recordings used for this purpose at any time.
Can Alexa be hacked or misused by others?
It’s unlikely, but possible. In the past, researchers found certain vulnerabilities in Alexa devices that could allow attackers to hack into them to spread malware or steal personal details. Amazon has since taken steps to address those issues and continues to monitor and improve Alexa’s code, but as with any connected device, new exploits could still emerge in the future.
Can using Alexa devices compromise your data?
 Alexa devices and other smart speakers work by recording data and sending it to servers for processing, so there’s always a small risk that it could be compromised or accessed by unauthorized parties..
Alexa devices and other smart speakers work by recording data and sending it to servers for processing, so there’s always a small risk that it could be compromised or accessed by unauthorized parties..
The same principle applies to information you submit when signing up for online accounts or sharing your email with a digital service. Using Alexa isn’t significantly riskier than these activities, but it also cannot be considered entirely risk-free.
Data collection and cloud processing
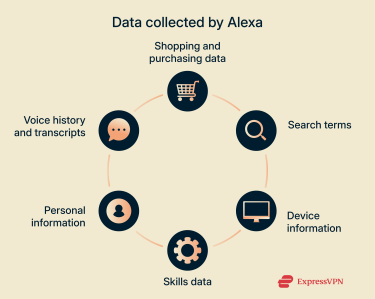
Like other major tech companies, Amazon can use its devices to collect various pieces of user data. However, since Alexa devices primarily function through audio and voice recognition, they’re capable of collecting a broader mix of behavioral and environmental data than everyday web services.
This data can include voice history, transcripts of your interactions, purchase data, search queries, information about the devices you use, data from any Alexa skills you enable, and personal information, such as your name, location, and Amazon profile details.
All of this data can be stored and processed on Amazon’s cloud servers. The only things that aren’t uploaded to the cloud are images or videos captured from Echo Show devices; they are processed locally.
Common misunderstandings
- Alexa processes voice commands locally: While it was once possible for Amazon Alexa devices to process your audio input locally, that feature was discontinued in March 2025. Now, every time you interact with Alexa, your data gets sent to the cloud.
- Alexa is always recording: As long as the device is powered on and the microphone is enabled, Alexa will always listen for its wake word, but, according to Amazon, it isn’t spying or recording what you say.
- Alexa only activates with user consent: Technically, Alexa does only activate with user consent. However, the device may occasionally activate and record conversations if it misinterprets background sounds, such as TV or radio, as its wake word. This is a limitation shared by other voice-activated devices, including Siri and Google Assistant.
- Amazon sells Alexa data: Amazon officially states that it does not sell Alexa data. However, the company does share certain data with other businesses and can use it for a variety of purposes, though not for profit.
Real-world incidents
As of November 2025, there have been no widespread Amazon Alexa data breaches; however, the company did face a lawsuit in 2023 filed by the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) regarding its data collection practices. Amazon agreed to settle the case for $25 million.
How to stop Alexa from listening or recording
 The simplest option to stop an Alexa device from listening or recording is to mute its microphone. You can press the Mute button on any Echo Dot or other device to temporarily mute it, and until you unmute the mic, your Alexa device will not be able to hear or record anything you say. Alternatively, you can adjust Alexa’s settings to control what it does with your data.
The simplest option to stop an Alexa device from listening or recording is to mute its microphone. You can press the Mute button on any Echo Dot or other device to temporarily mute it, and until you unmute the mic, your Alexa device will not be able to hear or record anything you say. Alternatively, you can adjust Alexa’s settings to control what it does with your data.
Adjust Alexa’s privacy settings
You can access Alexa’s privacy settings at any time via the official Alexa app or website. There, you’ll be able to review your voice history, delete voice recordings, control how long Amazon is allowed to store your voice data on its cloud servers, or even instruct Alexa not to save any recordings (which means they will be automatically deleted as soon as they’ve been processed and replied to).
Limit third-party access with skills permissions
In the Alexa Privacy menu, you can find options to control which pieces of information (if any) skills developers have access to.
Use voice profiles for safer use
Alexa’s Voice ID feature helps the system more effectively recognize and respond to your specific voice and commands. Creating individual IDs for each user should therefore help you enjoy a more personalized experience and potentially encounter fewer incidents of false triggers.
Building trust: Amazon, Alexa, and transparency
Major tech firms like Amazon take significant steps to safeguard user data, including the use of encryption and secure servers. They also offer security updates to fix any identified issues and privacy settings for users to feel more in control of their data and experiences.
How Amazon addresses privacy concerns
Amazon uses strong security systems, including advanced encryption algorithms, to keep user data safe and minimize the risk of leaks and breaches. It is compliant with leading industry standards and data regulations and provides users with an array of controls, options, and opt-out switches to set their own privacy preferences across the devices they use.
The company also has a strong track record in terms of fixing any weaknesses that emerge in its systems. For example, in 2020, when cybersecurity firm Check Point discovered a weakness in the Alexa code that could have allowed hackers to access personal data or install malicious skills, Amazon acted swiftly to solve the problem.
Steps you can take to feel in control
- Regularly review your voice history in the Amazon Alexa app so you know exactly when your device activates and what it recorded.
- Set your voice recordings to either delete automatically after processing or after a set period of time, like 3 months.
- Position your Amazon Alexa devices in rooms where you feel comfortable with them recording, like the living room or kitchen, rather than bedrooms or bathrooms.
- Disable and remove any skills you don’t need, and only install skills that offer some sort of value to you.
- Use voice commands on a regular basis to instruct Alexa to delete your most recent recordings.
- Hit the Mute button on your Alexa device whenever you want to speak freely without worrying about Alexa picking up any false triggers.
- Install a VPN on your devices or on your router for network-wide encryption and stronger online privacy. While this won’t stop Amazon from processing your data, it can help protect your connection from cybercriminals who might try to intercept your internet traffic or access other data on your network.
FAQ: Common questions about Alexa
Can Alexa record without you knowing?
Alexa is designed to only start recording when it hears its wake word, like “Alexa” or “Echo,” so it should never record unless you tell it to. However, there are cases when the device may inadvertently activate due to a “false trigger,” like a bit of background noise that sounds like the wake word. In these cases, the device should only record a small snippet of audio before going back to sleep.
If you have an Alexa device with a camera, you should know that all processing of camera input is done locally on the device. No video or images are sent to the cloud.
Is Alexa safe to keep in the bedroom?
Opinions vary on this subject, but many tech experts believe that it’s best to use Alexa in spaces like the living room or kitchen and avoid installing Alexa devices in more intimate spaces, like the bedroom or bathroom. This is because, even though Alexa is designed to only activate when you tell it to, there may be cases when it listens to your conversations inadvertently due to false triggers.
What privacy settings should I change first?
It depends on your needs and preferences, but from a privacy point of view, many cybersecurity experts recommend either disabling or restricting the voice recordings that Amazon uses to improve customer experience. You can manage these settings directly in the Alexa app or website.
Can someone hack into my Alexa device?
It’s technically possible, yes. There was an incident in 2020 when a flaw in Alexa software was discovered, which could have allowed hackers access to data on the device, including its users’ personal information and conversation history. Fortunately, Amazon acted swiftly to fix this flaw, but it’s not impossible that other exploits could be uncovered in the future.
How to permanently delete Alexa data?
You can use the Alexa app or website to delete all of your Alexa data, including voice history and connected devices.
Take the first step to protect yourself online. Try ExpressVPN risk-free.
Get ExpressVPN